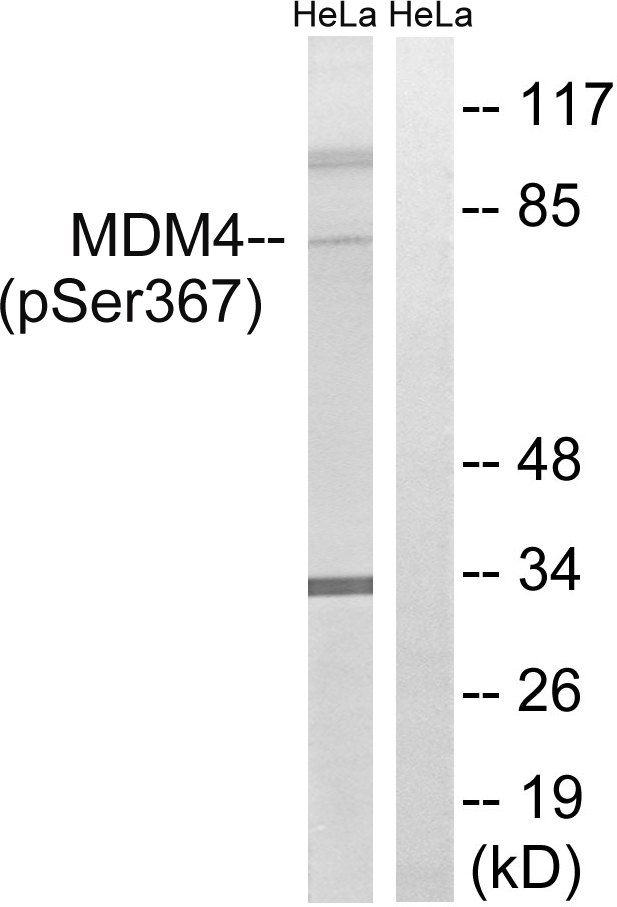
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
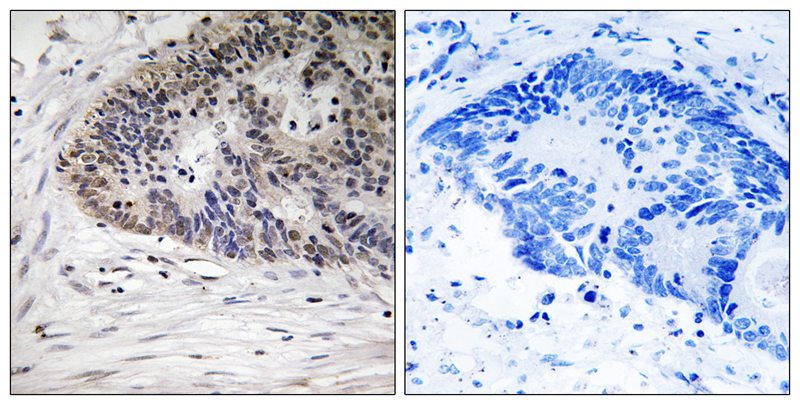
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | double minute 4 protein; Mdm2-like p53-binding protein; MDMX; p53-binding protein Mdm4 |
| Entrez GeneID | 4194; |
| WB Predicted band size | 80kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Peptide sequence around phosphorylation site of serine 367 (T-I-S(p)-A-P) derived from Human MDM4. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于MDM4 (Phospho-Ser367)抗体的3篇参考文献的简要整理,包含文献名称、作者及摘要内容概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Phosphorylation of MDMX Mediated by Akt Leads to Stabilization and Induces 14-3-3 Binding*
**作者**:Li X., Chen J., Lu Z.
**摘要**:研究揭示Akt激酶介导MDMX在Ser367位点的磷酸化,增强其稳定性并促进与14-3-3蛋白的结合,从而抑制p53活性。实验中利用Phospho-Ser367特异性抗体验证了DNA损伤后该位点的磷酸化动态。
2. **文献名称**:*Regulation of MDM4 Activity by Phosphorylation: A Structural Perspective*
**作者**:Wade M., Wang Y., Wahl G.M.
**摘要**:通过结构生物学分析MDM4磷酸化对其功能的影响,重点讨论Ser367磷酸化对抗原表位的影响。研究使用Phospho-Ser367抗体证明该修饰在肿瘤细胞中调控MDM4与p53的相互作用。
3. **文献名称**:*Development of a Phospho-Specific Antibody for Detecting MDM4 Serine 367 Phosphorylation in Human Cancers*
**作者**:Okamoto K., Kamata H., Karin M.
**摘要**:报道了一种针对MDM4 Ser367磷酸化位点的多克隆抗体的开发与验证,证明其在乳腺癌和肺癌组织中特异性检测该修饰的可靠性,并揭示其与患者预后的相关性。
---
以上文献均涉及MDM4 Ser367磷酸化的功能研究或抗体应用,具体实验细节可通过数据库(如PubMed)进一步检索全文。若需更多文献,可调整关键词或扩展时间范围进行查找。
The MDM4 (Phospho-Ser367) antibody is a specialized tool used to detect the phosphorylation of MDM4 (also called MDMX) at serine residue 367. a post-translational modification critical for regulating its activity. MDM4 is a key negative regulator of the tumor suppressor p53. functioning in tandem with MDM2 to control p53 stability and transcriptional activity under normal conditions. Phosphorylation at Ser367 occurs in response to cellular stress, such as DNA damage, and is mediated by kinases like ATM/ATR. This modification promotes MDM4 degradation or alters its interaction with MDM2. ultimately relieving p53 inhibition and enabling p53-dependent cell cycle arrest or apoptosis.
The antibody is widely used in cancer research to study mechanisms underlying p53 pathway dysregulation, particularly in tumors with wild-type p53 but compromised activity due to MDM4 overexpression. It helps assess MDM4 phosphorylation status in experimental models, including cell lines or tissues treated with genotoxic agents, and may inform therapeutic strategies targeting the MDM4-p53 axis. Applications include Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunofluorescence. Validating its specificity is essential, as cross-reactivity with homologous proteins (e.g., MDM2) or non-phosphorylated MDM4 could lead to misinterpretation. Understanding MDM4 phosphorylation dynamics provides insights into cellular stress responses and potential biomarkers for cancer treatment efficacy.
×