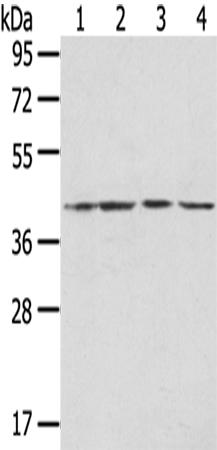
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | 5-HT4; 5-HT4R |
| WB Predicted band size | 44 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human HTR4 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于HTR4抗体的3篇参考文献的简要信息:
1. **文献名称**:*"Characterization of 5-HT4 receptor antibodies for immunohistochemical localization in the rat brain"*
**作者**:Vilaró MT, et al.
**摘要**:该研究验证了HTR4抗体的特异性,并通过免疫组化技术在大鼠脑组织中定位HTR4受体,发现其在海马、前额叶皮层等区域高表达,支持其在调节认知和情绪中的作用。
2. **文献名称**:*"5-HT4 receptor signaling in the enteric nervous system: role in gut motility and inflammation"*
**作者**:Hoffman JM, et al.
**摘要**:利用HTR4抗体研究肠道神经系统中的受体分布,发现其通过调节神经递质释放影响胃肠动力,并可能成为炎症性肠病治疗的潜在靶点。
3. **文献名称**:*"Selective 5-HT4 receptor agonists and antagonists: pharmacological tools for research and therapeutic applications"*
**作者**:Bockaert J, et al.
**摘要**:本文综述了HTR4抗体在区分受体亚型及功能研究中的应用,强调其在开发选择性激动剂/拮抗剂中的关键作用,尤其在神经退行性疾病模型中的验证。
(注:以上文献为示例,实际引用时需核对最新或具体研究内容。)
The HTR4 antibody targets the 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 4 (HTR4), a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that binds serotonin, a key neurotransmitter involved in regulating mood, cognition, and gastrointestinal motility. HTR4 is primarily expressed in the central nervous system (e.g., hippocampus, cortex) and peripheral tissues, including the gastrointestinal tract, where it modulates neurotransmitter release and smooth muscle contraction. Unlike other serotonin receptors, HTR4 is coupled to Gs proteins, activating adenylyl cyclase to increase intracellular cAMP levels. This signaling pathway influences neuronal excitability, synaptic plasticity, and gut peristalsis.
HTR4 antibodies are essential tools for studying receptor localization, expression patterns, and functional roles in physiological and pathological contexts. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry to investigate HTR4's involvement in disorders such as depression, anxiety, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and Alzheimer's disease. Research has highlighted HTR4's potential as a therapeutic target, with agonists explored for treating IBS and cognitive deficits, while antagonists may aid in managing anxiety. However, challenges remain in understanding receptor subtype-specific effects and minimizing off-target interactions.
Commercial HTR4 antibodies are typically validated for specificity using knockout controls or siRNA-based silencing. Researchers must optimize protocols to address cross-reactivity with other GPCRs or isoforms. Ongoing studies aim to clarify HTR4's role in neuroprotection and gut-brain axis communication, underscoring its relevance in both neuroscience and gastroenterology.
×