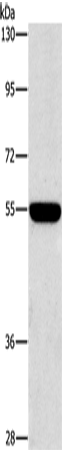
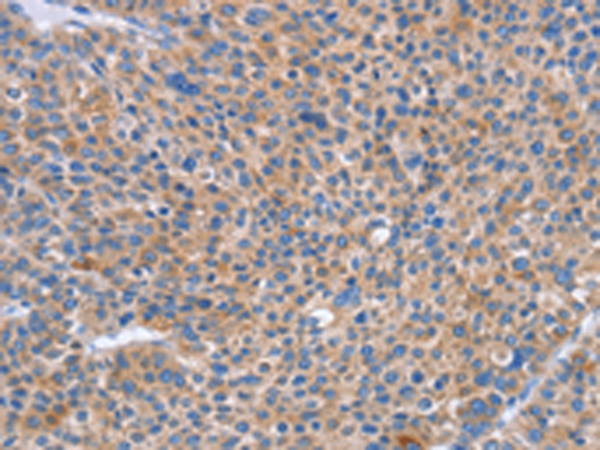
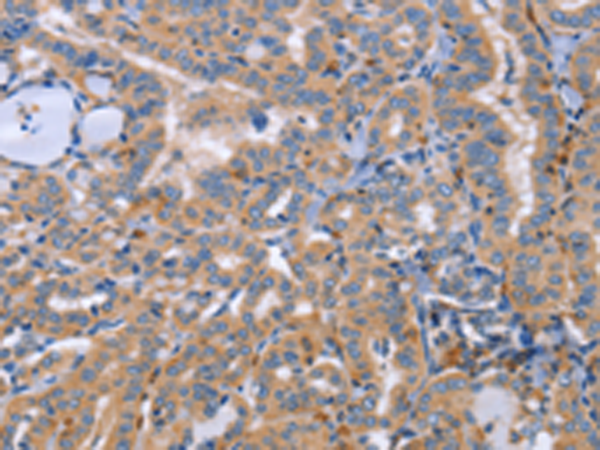
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | p75; QA79; AIRM1; CD328; CDw328; D-siglec; SIGLEC-7; SIGLECP2; SIGLEC19P; p75/AIRM1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 51 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human SIGLEC7 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于SIGLEC7抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **"Siglec-7 Antibody-Dependent NK Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity Against Cancer Cells"**
- **作者**: Ito A. et al.
- **摘要**: 研究报道了靶向SIGLEC7的单克隆抗体通过阻断其与唾液酸配体的免疫抑制性信号,增强自然杀伤(NK)细胞对肿瘤细胞的杀伤活性,为癌症免疫治疗提供新策略。
2. **"Siglec-7 as a Novel Immune Checkpoint Molecule on Myeloid Cells"**
- **作者**: Crocker P.R. et al.
- **摘要**: 文章揭示了SIGLEC7在髓系细胞上的表达及其在肿瘤微环境中的免疫抑制功能,使用特异性抗体阻断SIGLEC7可逆转髓系抑制细胞(MDSCs)对T细胞的抑制作用。
3. **"Targeting Siglec-7 with Monoclonal Antibodies Enhances Phagocytosis of Opsonized Bacteria"**
- **作者**: Chen G.Y. et al.
- **摘要**: 该研究开发了一种抗SIGLEC7的激动型抗体,证明其可通过激活巨噬细胞表面的SIGLEC7信号通路,促进对病原体的吞噬作用,为抗感染治疗提供潜在工具。
如需具体文献来源或更多信息,建议通过PubMed或期刊数据库查询完整论文。
**Background of SIGLEC7 Antibody**
SIGLEC7 (sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-type lectin 7) is a transmembrane protein belonging to the SIGLEC family of immune-regulatory receptors, primarily expressed on natural killer (NK) cells, monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells. It contains an N-terminal V-set immunoglobulin (Ig) domain that recognizes sialylated glycans on target cells, followed by multiple C2-set Ig domains, a transmembrane region, and a cytoplasmic tail with immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motifs (ITIMs). These motifs enable SIGLEC7 to transmit inhibitory signals, dampening immune cell activation upon ligand binding, thus playing a role in immune tolerance and homeostasis.
SIGLEC7 interacts with sialic acid-rich ligands on pathogens, tumor cells, or host tissues. Its engagement can suppress NK cell cytotoxicity and cytokine production, contributing to immune evasion in cancers or chronic infections. Dysregulated SIGLEC7 expression or function has been implicated in diseases like cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and viral infections.
Antibodies targeting SIGLEC7 are pivotal tools for studying its expression, ligand interactions, and signaling mechanisms. They are used in flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and functional assays to dissect its role in immune modulation. Therapeutic anti-SIGLEC7 antibodies are under exploration to either block inhibitory signals (enhancing anti-tumor immunity) or mimic ligand binding (suppressing hyperactive immune responses in autoimmune conditions). These antibodies vary in specificity, recognizing different epitopes or isoforms, and their applications depend on intended agonistic or antagonistic effects.
(Word count: 246)
×