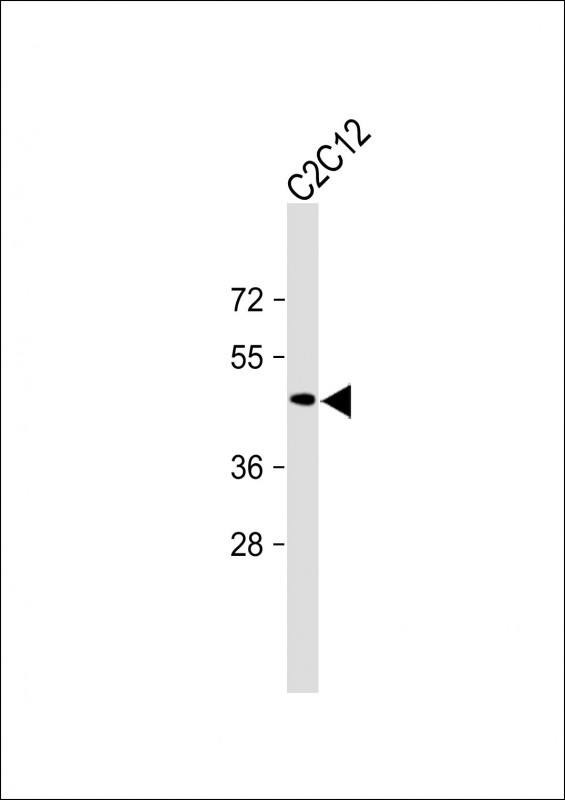
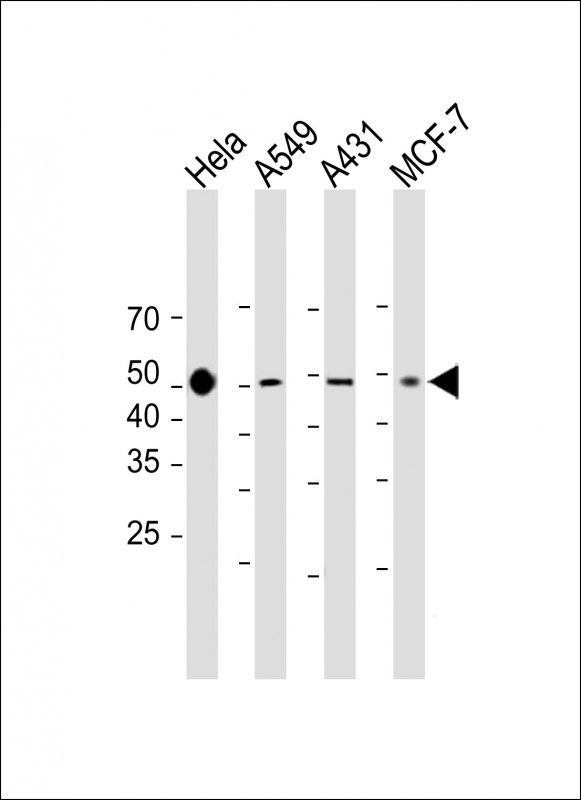
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1, PD-L1, PDCD1 ligand 1, Programmed death ligand 1, hPD-L1, B7 homolog 1, B7-H1, CD274 |
| Entrez GeneID | 29126 |
| WB Predicted band size | 33.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This PD L1 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between amino acids from the human region of human PD L1. |
+ +
以下是3-4篇关于PD-L1抗体的参考文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Pembrolizumab versus Ipilimumab in Advanced Melanoma*
**作者**:Robert, C. et al.
**摘要**:该研究(KEYNOTE-006)比较了PD-1抗体Pembrolizumab与CTLA-4抗体Ipilimumab在晚期黑色素瘤患者中的疗效。结果显示,Pembrolizumab显著延长无进展生存期和总生存期,且安全性更优,支持PD-1/PD-L1通路抑制在肿瘤免疫治疗中的核心地位。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Nivolumab and Ipilimumab versus Ipilimumab in Untreated Melanoma*
**作者**:Wolchok, J.D. et al.
**摘要**:CheckMate 067临床试验评估了Nivolumab(PD-1抗体)单药或联合Ipilimumab治疗晚期黑色素瘤的效果。联合治疗组客观缓解率和生存率显著优于单药组,但毒性增加,提示PD-L1/PD-1阻断联合其他免疫疗法可能增强抗肿瘤活性。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Atezolizumab in Platinum-Treated Locally Advanced or Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma*
**作者**:Powles, T. et al.
**摘要**:该研究(IMvigor210)评估了PD-L1抗体Atezolizumab在铂类化疗失败的膀胱癌患者中的疗效。结果显示,肿瘤PD-L1高表达患者的总生存期显著延长,证实PD-L1表达水平可作为生物标志物指导治疗选择。
---
4. **文献名称**:*Atezolizumab and Nab-Paclitaxel in Advanced Triple-Negative Breast Cancer*
**作者**:Adams, S. et al.
**摘要**:IMpassion130试验探索了Atezolizumab(PD-L1抗体)联合白蛋白紫杉醇治疗三阴性乳腺癌的效果。联合治疗显著延长PD-L1阳性患者的无进展生存期,首次证明免疫治疗在该亚型乳腺癌中的临床价值。
---
以上文献均发表于*New England Journal of Medicine*或*Lancet Oncology*等权威期刊,聚焦PD-L1抗体在肿瘤免疫治疗中的关键作用及临床转化研究。
PD-L1 (programmed death-ligand 1) is a transmembrane protein expressed on cancer cells and immune cells, playing a critical role in suppressing the immune system. It binds to PD-1 receptors on T cells, delivering inhibitory signals that dampen T-cell activation, proliferation, and cytotoxic function, enabling tumors to evade immune surveillance. Targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 axis with monoclonal antibodies has revolutionized cancer immunotherapy by blocking this interaction, thereby restoring anti-tumor immunity.
The development of PD-L1 antibodies began in the early 2000s, driven by the need to overcome tumor-induced immune tolerance. Key drugs like atezolizumab (Tecentriq), durvalumab (Imfinzi), and avelumab (Bavencio) were designed to bind PD-L1. preventing its interaction with PD-1 and CD80. These antibodies have shown efficacy in various cancers, including non-small cell lung cancer, urothelial carcinoma, and melanoma. Their clinical success hinges on biomarker-driven strategies, as PD-L1 expression levels (assessed via immunohistochemistry) often correlate with treatment response. However, limitations exist, such as variable assay standardization and tumor heterogeneity.
Current research focuses on combination therapies (e.g., with chemotherapy, radiation, or other immunotherapies) to enhance efficacy, and on developing next-generation agents like bispecific antibodies or antibody-drug conjugates. Despite challenges, PD-L1 antibodies remain cornerstone therapies in immuno-oncology, exemplifying the shift toward precision medicine in cancer treatment.
×