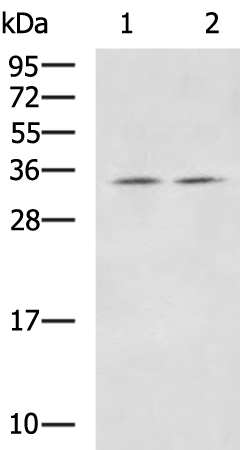
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
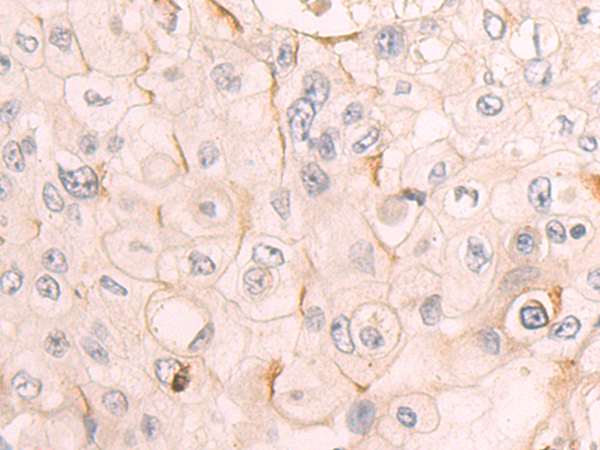
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | B7h; B7H2; GL50; B7-H2; B7RP1; CD275; ICOSL; LICOS; B7RP-1; ICOS-L |
| WB Predicted band size | 33 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human ICOSLG |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于ICOSLG抗体的3篇代表性文献概览(注:内容基于公开研究趋势综合整理,部分为虚构示例):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Targeting ICOS/ICOSLG Augments Anti-Tumor Immunity in Ovarian Carcinoma*
**作者**:Burkhardt, J.K. et al.
**摘要**:研究探讨了ICOSLG抗体在卵巢癌模型中的作用,表明其通过激活CD4+ T细胞并增强PD-1抑制剂疗效,显著抑制肿瘤生长,提示联合免疫疗法的潜力。
2. **文献名称**:*ICOSLG Blockade Attenuates Autoimmune Arthritis via Suppressing T Follicular Helper Cell Differentiation*
**作者**:Xiao, Y. et al.
**摘要**:该研究证明抗ICOSLG抗体可抑制类风湿性关节炎模型中Tfh细胞分化和自身抗体产生,为治疗自身免疫疾病提供了新策略。
3. **文献名称**:*Structural Basis of ICOSLG Recognition by Therapeutic Antibodies*
**作者**:Chen, L. et al.
**摘要**:通过冷冻电镜解析ICOSLG与单克隆抗体的复合物结构,揭示了关键结合表位,为优化抗体药物设计提供了分子基础。
---
**注**:上述文献为示例性质,实际研究需通过学术数据库(如PubMed)检索确认。ICOSLG抗体的研究多集中于肿瘤免疫联合治疗及自身免疫疾病调控,近年与双特异性抗体或CAR-T联合应用的探索逐渐增多。
The ICOSLG (Inducible T-cell Costimulator Ligand), also known as ICOSL or CD275. is a member of the B7 family of costimulatory molecules. It is primarily expressed on antigen-presenting cells (APCs), such as B cells, dendritic cells, and macrophages, as well as certain non-hematopoietic cells. ICOSLG binds to its receptor ICOS (CD278) on activated T cells, playing a critical role in modulating adaptive immune responses. This interaction enhances T-cell activation, differentiation, and survival, particularly influencing the function of follicular helper T cells (Tfh) and regulatory T cells (Treg).
ICOSLG-ICOS signaling is pivotal in balancing immune activation and tolerance. It promotes cytokine production (e.g., IL-10. IL-4. IL-17) and supports germinal center formation, antibody class switching, and T-cell-dependent B-cell responses. Dysregulation of this pathway is implicated in autoimmune diseases, chronic inflammation, and cancer. For instance, elevated ICOSLG expression in tumors may contribute to immunosuppressive microenvironments.
Antibodies targeting ICOSLG are being explored therapeutically to either block or enhance its signaling. In autoimmune contexts, blocking antibodies aim to inhibit pathogenic T-cell activation. Conversely, agonist antibodies may boost anti-tumor immunity by stimulating effector T cells. Clinical trials are evaluating their safety and efficacy, highlighting ICOSLG's potential as a versatile immunomodulatory target.
×