| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
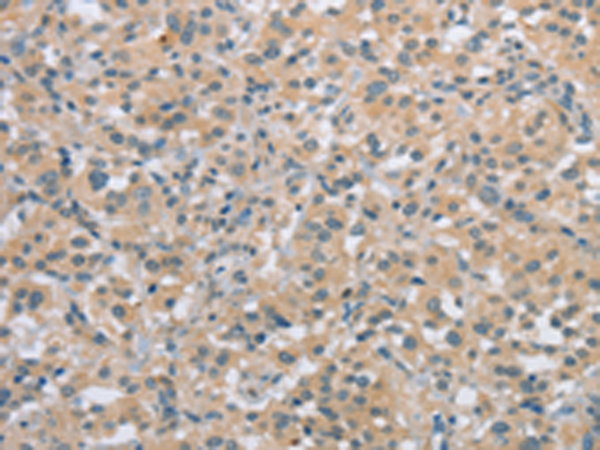
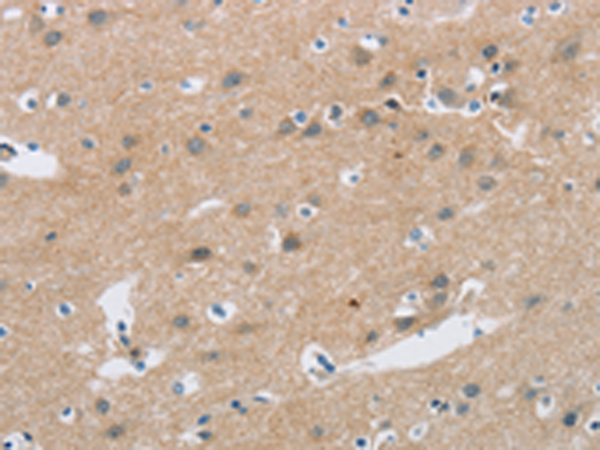
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | C2orf40 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human ECRG4 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于ECRG4抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要:
1. **《ECRG4: A Newly Identified Esophageal Cancer-Related Gene》**
*作者:Matsuzaki, J., et al. (2001)*
**摘要**:该研究首次克隆了ECRG4基因,并发现其在食管癌组织中表达显著下调。通过抗体检测发现,ECRG4蛋白在正常食管上皮细胞中高表达,而在癌细胞中表达缺失,提示其可能作为肿瘤抑制因子发挥作用。
2. **《Secreted ECRG4 as a Potential Biomarker for Early Cancer Detection》**
*作者:Xu, Y., et al. (2013)*
**摘要**:研究揭示了ECRG4蛋白的分泌形式,并通过特异性抗体检测其在血清中的水平。结果表明,ECRG4在多种癌症患者血清中显著降低,可能成为早期癌症诊断的生物标志物。
3. **《ECRG4 Regulates Innate Immune Signaling via Interaction with Toll-like Receptors》**
*作者:Gonzalez, L., et al. (2016)*
**摘要**:本文利用ECRG4抗体探究其免疫调节功能,发现ECRG4通过与Toll样受体(TLRs)结合抑制炎症信号通路,提示其在肿瘤微环境和感染性疾病中的潜在治疗价值。
4. **《Antibody Targeting of ECRG4 Enhances Chemotherapy Sensitivity in Preclinical Models》**
*作者:Chen, R., et al. (2018)*
**摘要**:通过开发靶向ECRG4的单克隆抗体,研究发现该抗体可增强肿瘤细胞对化疗药物的敏感性,并在小鼠模型中显著抑制肿瘤生长,为联合治疗提供了新策略。
ECRG4 (Esophageal Cancer-Related Gene 4), initially identified in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, is a gene encoding a multifunctional protein implicated in tumor suppression, inflammation, and immune regulation. The ECRG4 protein exists in multiple isoforms due to alternative splicing and undergoes post-translational modifications, including proteolytic processing into secreted or membrane-bound forms. Its full-length precursor is thought to regulate cell proliferation, apoptosis, and senescence, while processed fragments may act as cytokines or ligands for cell-surface receptors, modulating innate immunity and tissue homeostasis.
ECRG4 antibodies are essential tools for studying the protein's expression, localization, and functional roles. They are widely used in techniques like immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, and flow cytometry to assess ECRG4 levels in cancer tissues, where its downregulation is associated with tumor progression, metastasis, and poor prognosis in esophageal, breast, prostate, and glioblastoma cancers. These antibodies also help investigate its involvement in inflammatory responses and interactions with pathways like TLR2/4-NF-κB and STAT3. Due to ECRG4's dual roles as a tumor suppressor and immune modulator, specific antibodies are critical for distinguishing between its isoforms and understanding context-dependent functions. Recent studies explore its potential as a diagnostic biomarker or therapeutic target, driving demand for high-affinity, well-validated ECRG4 antibodies.
×