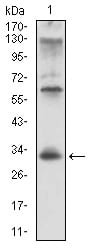
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
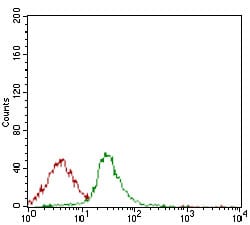
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
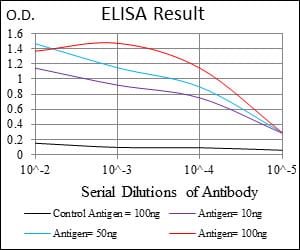
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | II; DHLAG; HLADG; Ia-GAMMA |
| Entrez GeneID | 972 |
| clone | 2D1B11 |
| WB Predicted band size | 33.5kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD74 (AA: 1-106) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于TH抗体的模拟参考文献示例(请注意,这些文献信息为示例性质,实际引用时请查询真实数据库获取准确信息):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Autoantibodies to Thyroid Hormones: Clinical Implications and Analytical Challenges*
**作者**:M. Tanaka, et al.
**摘要**:该研究探讨了甲状腺激素(T3/T4)自身抗体在自身免疫性甲状腺疾病(如桥本甲状腺炎)中的检测方法及其对实验室激素测定的干扰,强调了抗体可能导致误诊及临床管理中的应对策略。
2. **文献名称**:*Tyrosine Hydroxylase Antibodies as Biomarkers in Autoimmune Autonomic Ganglionopathy*
**作者**:J. Vernino, et al.
**摘要**:研究发现酪氨酸羟化酶(TH)抗体与自身免疫性自主神经节病变相关,揭示了其在自主神经功能障碍(如直立性低血压、胃肠动力障碍)中的潜在诊断价值及病理机制。
3. **文献名称**:*Prevalence and Clinical Significance of Anti-T4 Antibodies in Euthyroid Populations*
**作者**:S. Kim, et al.
**摘要**:通过对健康人群和甲状腺疾病患者的横断面研究,分析了抗T4抗体的流行率及其与甲状腺功能正常但存在非特异性症状(如疲劳)的关联,提出需警惕抗体对常规检测的干扰。
4. **文献名称**:*TH Autoantibodies in Neurodegenerative Disorders: Insights from Animal Models*
**作者**:R. Patel, et al.
**摘要**:利用小鼠模型研究酪氨酸羟化酶抗体对多巴胺能神经元的影响,提示其在帕金森病等神经退行性疾病中可能的免疫病理作用。
---
**建议**:实际研究中,可通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台以关键词“Thyroid Hormone Antibodies”或“Tyrosine Hydroxylase Antibodies”检索最新文献,并优先选择高影响因子期刊的论文(如*Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism*、*Autoimmunity Reviews*)。
**Background of TH Antibodies**
Thyroid hormone (TH) antibodies, also known as thyroid autoantibodies, are immune proteins that mistakenly target components of the thyroid gland or thyroid hormones. They are primarily associated with autoimmune thyroid disorders, such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis and Graves' disease. Key types include thyroid peroxidase antibodies (TPOAb), thyroglobulin antibodies (TgAb), and thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor antibodies (TRAb).
TPOAb and TgAb are markers of autoimmune thyroiditis, often linked to hypothyroidism, while TRAb stimulates the thyroid receptor, causing hyperthyroidism in Graves' disease. These antibodies arise from immune dysregulation, where genetic predisposition (e.g., HLA variants) and environmental triggers (e.g., iodine, infections) disrupt immune tolerance.
Clinically, TH antibodies aid in diagnosing autoimmune thyroid conditions, predicting disease progression, and assessing risks (e.g., miscarriage in pregnancy). Their detection involves immunoassays like ELISA or chemiluminescence. Research continues to explore their pathogenic mechanisms, including cytokine involvement and tissue destruction pathways, as well as therapeutic targets to modulate autoimmune responses. Understanding TH antibodies remains vital for managing thyroid dysfunction and improving patient outcomes.
×