| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
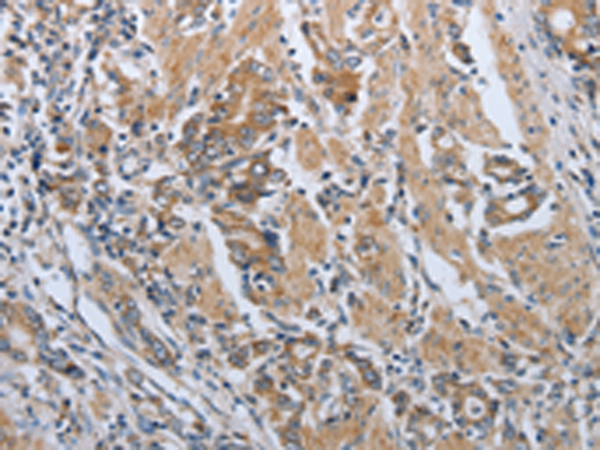
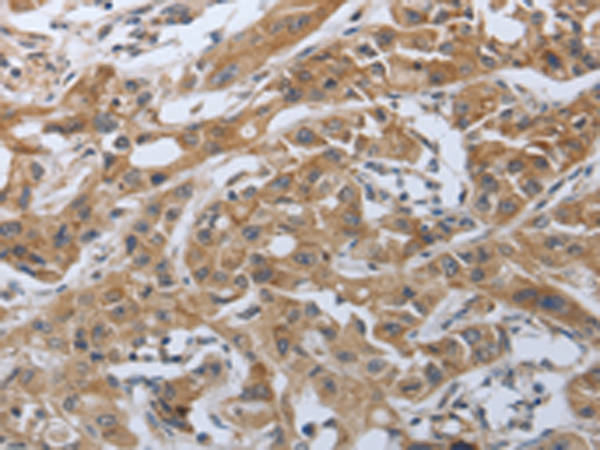
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | PD1, PD-1, CD279, SLEB2, hPD-1, hPD-l |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human PDCD1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于PDCD1(PD-1)抗体的经典文献概览:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Safety and Activity of Anti-PD-1 Antibody in Cancer*
**作者**:Topalian SL, et al.
**期刊/年份**:*New England Journal of Medicine* (2012)
**摘要**:该研究首次报道了抗PD-1单抗(nivolumab)在晚期黑色素瘤、非小细胞肺癌和肾细胞癌患者中的临床试验结果,证明其显著抗肿瘤活性且安全性可控,为PD-1抗体临床应用奠定了基础。
2. **文献名称**:*Pembrolizumab versus Chemotherapy for PD-L1–Positive Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer*
**作者**:Robert C, et al.
**期刊/年份**:*New England Journal of Medicine* (2015)
**摘要**:研究显示,针对PD-L1高表达的非小细胞肺癌患者,PD-1抗体pembrolizumab较传统化疗显著延长无进展生存期,确立了PD-1抗体作为生物标志物指导的精准治疗策略。
3. **文献名称**:*PD-1 Blockade in Tumors with Mismatch-Repair Deficiency*
**作者**:Le DT, et al.
**期刊/年份**:*New England Journal of Medicine* (2015)
**摘要**:该研究首次证明,抗PD-1抗体(pembrolizumab)在具有错配修复缺陷(dMMR)的多种实体瘤中具有显著疗效,揭示了肿瘤基因组特征与PD-1抗体治疗响应的关联。
---
这些文献涵盖了PD-1抗体的关键临床试验、疗效验证及生物标志物研究,对癌症免疫治疗发展具有里程碑意义。
PDCD1 (programmed cell death protein 1) is a gene encoding the PD-1 receptor, an immune checkpoint protein expressed on activated T cells, B cells, and myeloid cells. As a key regulator of immune tolerance, PD-1 interacts with its ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2 to inhibit T-cell activation, preventing excessive immune responses and autoimmune damage. However, many cancers exploit this pathway by overexpressing PD-L1 to suppress antitumor immunity, enabling immune evasion.
PDCD1-targeted antibodies, known as PD-1 inhibitors, block this interaction, restoring T-cell-mediated tumor destruction. Developed as part of immune checkpoint inhibitor therapies, these antibodies (e.g., nivolumab, pembrolizumab) have revolutionized cancer treatment. Approved for melanoma, lung cancer, and other malignancies, they demonstrate durable responses in subsets of patients. Their efficacy correlates with tumor PD-L1 expression and mutational burden, though responses vary widely.
Research continues to optimize PD-1 blockade through combination strategies (e.g., with CTLA-4 inhibitors or chemotherapy) and biomarker-driven patient selection. Challenges include managing immune-related adverse events and overcoming resistance mechanisms. As a cornerstone of immuno-oncology, PDCD1 antibodies exemplify the shift toward harnessing innate immunity against cancer, offering hope for previously untreatable cancers.
×