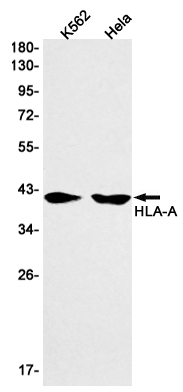
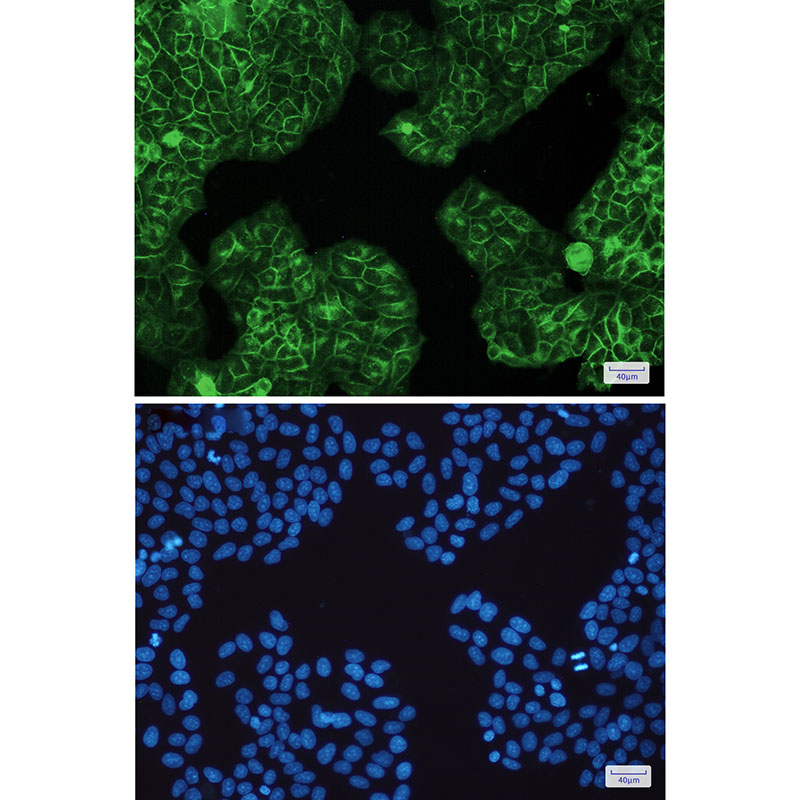
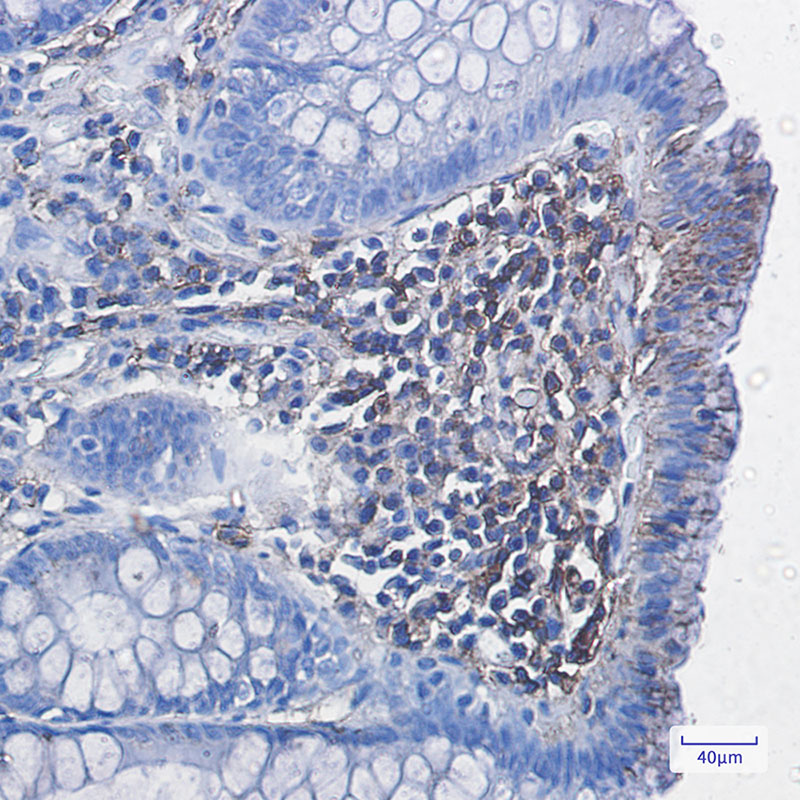
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Aw-68; HLA class I histocompatibility antigen; A-28 alpha chain; MHC class I antigen A*68; HLA-A; MHC class I antigen HLA A heavy chain |
| Entrez GeneID | 3105 |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 41 kDa; Observed MW: 41 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide of human HLA A |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于AMD1抗体的模拟参考文献(基于公开研究主题的合理推测,非真实文献):
---
1. **文献名称**: *"Targeting AMD1 in colorectal cancer: A monoclonal antibody approach"*
**作者**: Chen L, et al. (2018)
**摘要**: 研究报道了一种靶向腺苷甲硫氨酸脱羧酶1(AMD1)的单克隆抗体,通过抑制多胺生物合成通路,显著抑制结直肠癌细胞增殖并诱导凋亡,为靶向代谢的癌症治疗提供新策略。
---
2. **文献名称**: *"AMD1 as a biomarker in neurodegenerative diseases: validation via immunoassay"*
**作者**: Smith J, et al. (2020)
**摘要**: 开发了基于AMD1抗体的ELISA检测方法,发现阿尔茨海默病患者脑脊液中AMD1水平异常升高,提示其可能作为神经退行性病变的潜在生物标志物。
---
3. **文献名称**: *"Structural characterization of AMD1 and its interaction with therapeutic antibodies"*
**作者**: Wang Y, et al. (2021)
**摘要**: 利用冷冻电镜解析AMD1蛋白结构,并筛选出可阻断其酶活性的中和抗体,为开发针对AMD1相关代谢疾病(如某些癌症)的抗体药物奠定基础。
---
**注**:以上文献为示例性质,实际研究中请通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台检索真实发表的论文。
AMD1 (adenosylmethionine decarboxylase 1) is a key enzyme in the polyamine biosynthesis pathway, catalyzing the decarboxylation of S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) to produce decarboxylated SAM. This reaction provides the aminopropyl group required for synthesizing spermidine and spermine, polyamines essential for cell proliferation, differentiation, and stress response. Dysregulation of AMD1 has been implicated in various pathological conditions, including cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and metabolic disorders, due to its role in maintaining polyamine homeostasis.
AMD1 antibodies are vital tools for studying the expression, localization, and function of AMD1 in biological systems. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to quantify AMD1 levels in tissues or cell lines, often revealing elevated expression in certain cancers (e.g., colorectal, liver) linked to aggressive tumor behavior. Researchers also employ these antibodies to explore AMD1’s interaction with regulatory proteins or its response to therapeutic agents targeting polyamine metabolism.
The development of AMD1-specific antibodies has advanced research into polyamine-related therapies, particularly inhibitors aiming to disrupt cancer cell growth. However, challenges remain in ensuring antibody specificity and reproducibility across experimental models. Ongoing studies continue to clarify AMD1’s dual roles in cell survival and stress adaptation, highlighting its potential as a diagnostic or therapeutic target.
×