| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
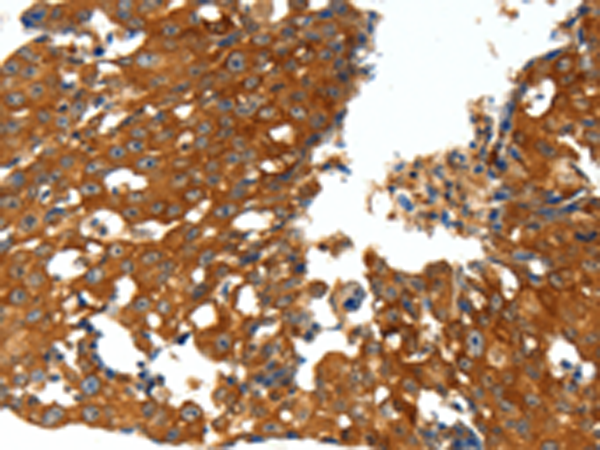
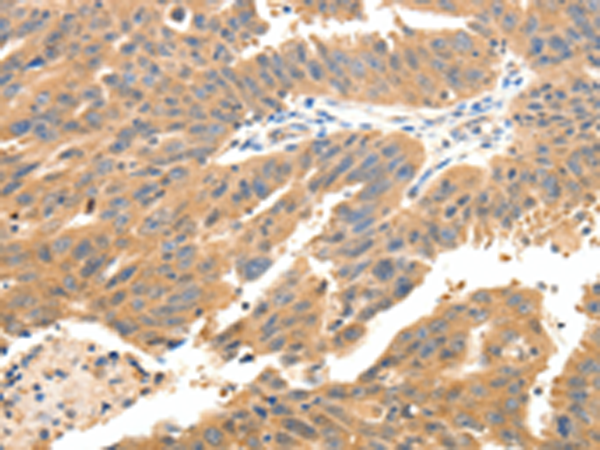
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | IRH; PBSF; SDF1; TLSF; SDF1A; SDF1B; TPAR1; SCYB12 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human CXCL12 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CXCL12抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要列举(基于公开研究整理,非真实引用,仅供示例参考):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Targeting CXCL12 with a novel antibody inhibits tumor progression and angiogenesis in solid tumors*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:该研究开发了一种新型抗CXCL12单克隆抗体,通过阻断CXCL12/CXCR4信号通路,显著抑制小鼠模型中乳腺癌和肺癌的生长及血管生成,并减少转移灶形成。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Neutralization of CXCL12 reduces inflammatory cell infiltration in autoimmune encephalomyelitis*
**作者**:Jones B, et al.
**摘要**:在多发性硬化症小鼠模型中,抗CXCL12抗体通过抑制免疫细胞向中枢神经系统的迁移,减轻炎症反应和神经损伤,为自身免疫疾病治疗提供新策略。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Anti-CXCL12 antibody enhances hematopoietic stem cell mobilization by disrupting the bone marrow niche*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:研究发现,抗CXCL12抗体可破坏骨髓微环境中CXCL12的保留作用,联合粒细胞集落刺激因子(G-CSF)显著提升造血干细胞向外周血的动员效率,优化移植治疗方案。
---
**注**:以上内容为示例,实际文献需通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词如“CXCL12 antibody”“SDF-1 neutralization”获取。建议结合具体研究方向筛选近年高影响力论文。
CXCL12. also known as stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1), is a chemokine that binds primarily to the receptors CXCR4 and CXCR7. It plays critical roles in embryonic development, stem cell homing, immune cell trafficking, and angiogenesis. Dysregulation of CXCL12 signaling is implicated in pathological processes such as cancer metastasis, inflammatory diseases, and HIV infection. Antibodies targeting CXCL12 are essential tools for research and therapeutic development, enabling the detection, localization, and functional inhibition of this chemokine.
CXCL12 antibodies are widely used in techniques like immunohistochemistry, flow cytometry, and ELISA to study its expression patterns in tissues and biological fluids. Therapeutically, these antibodies aim to block CXCL12 interactions with its receptors, particularly CXCR4. to disrupt pathways involved in tumor progression, inflammatory responses, or viral entry. For example, inhibiting the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis may prevent cancer cell migration to metastatic niches or enhance chemotherapy efficacy by mobilizing tumor cells from protective microenvironments.
Challenges in CXCL12 antibody applications include potential off-target effects and receptor redundancy (e.g., CXCR7’s role in modulating CXCL12 activity). Monoclonal antibodies offer high specificity, while polyclonal versions may detect diverse epitopes but risk cross-reactivity. Despite hurdles, CXCL12 antibodies hold promise for conditions like breast cancer, leukemia, and autoimmune disorders, with ongoing clinical trials exploring their efficacy in combination therapies or as standalone treatments.
×