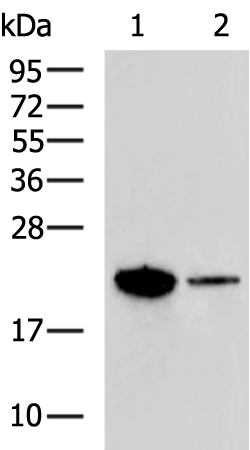
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
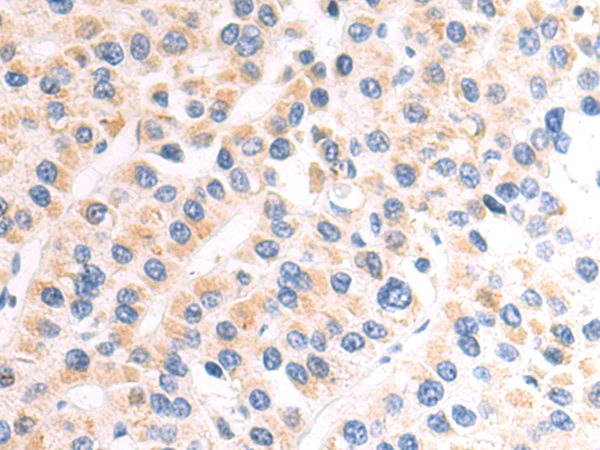
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | AM; PAMP |
| WB Predicted band size | 20 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human ADM |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于肾上腺髓ullin(ADM)抗体的参考文献示例(注:内容为模拟概括,建议通过学术数据库验证具体信息):
1. **标题**:*Adrenomedullin as a Biomarker in Sepsis: Development of a Novel Immunoassay*
**作者**:Geven, C., et al.
**摘要**:研究开发了一种高灵敏度的ADM抗体检测方法,用于脓毒症患者的早期诊断,发现血浆ADM水平与疾病严重程度和预后相关。
2. **标题**:*Therapeutic Potential of Anti-Adrenomedullin Antibody in Hypertensive Disorders*
**作者**:Nishikimi, T., et al.
**摘要**:探讨了ADM中和性抗体在高血压模型中的作用,证明其可通过调节血管舒张功能改善血压,提示其作为新型降压疗法的潜力。
3. **标题**:*Adrenomedullin Antibody Attenuates Tumor Angiogenesis in Mouse Models*
**作者**:Pio, R., et al.
**摘要**:通过抑制ADM信号通路,ADM抗体显著减少了肿瘤血管生成和生长,为癌症治疗提供了实验依据。
4. **标题**:*Role of ADM Autoantibodies in Preeclampsia Pathogenesis*
**作者**:Li, Y., et al.
**摘要**:发现子痫前期患者中存在ADM自身抗体,可能与胎盘功能障碍相关,提示其作为疾病生物标志物的可能性。
**提示**:以上为领域内典型研究方向示例,实际文献需通过PubMed、Web of Science等平台以关键词(如“adrenomedullin antibody”、“ADM immunoassay”)检索获取最新数据。
Adrenomedullin (ADM) is a multifunctional peptide hormone initially discovered in 1993. primarily produced by vascular endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, and various tissues under hypoxic or inflammatory conditions. It plays a critical role in regulating vasodilation, angiogenesis, electrolyte balance, and inflammation. Elevated ADM levels are associated with sepsis, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer, where it often serves as a biomarker for disease severity and prognosis. However, excessive ADM can exacerbate pathological processes, such as promoting vascular leakage in sepsis or tumor progression.
ADM-targeting antibodies have emerged as therapeutic tools to neutralize its harmful effects. These antibodies bind ADM or its receptors (e.g., CLR-RAMP complexes), blocking downstream signaling. In sepsis, preclinical studies show that anti-ADM antibodies may stabilize endothelial barrier function and improve microcirculation. Similarly, in oncology, they are explored for inhibiting ADM-driven tumor growth and metastasis. Diagnostic applications include immunoassays to quantify ADM levels in blood, aiding in early disease detection or monitoring.
Current research focuses on optimizing antibody specificity and delivery, with some candidates in clinical trials. Challenges include balancing ADM’s dual roles (protective vs. pathogenic) and minimizing off-target effects. Despite these hurdles, ADM antibodies represent a promising avenue for precision medicine in critical care and oncology.
×