
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
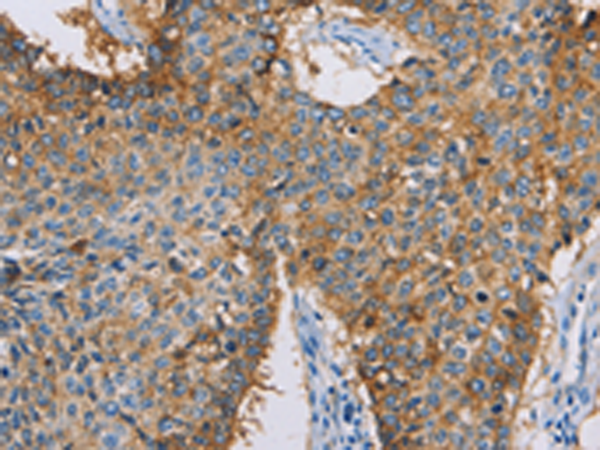
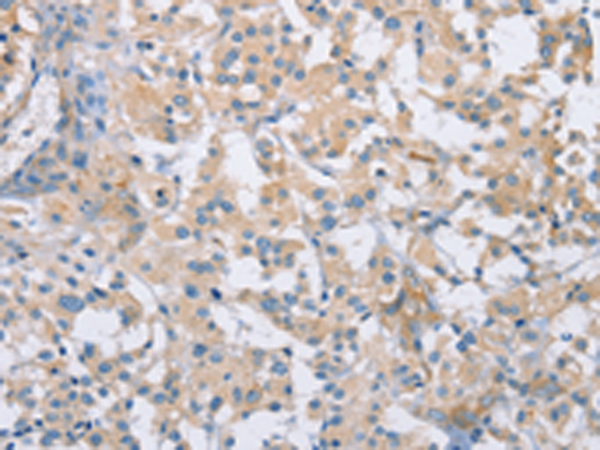
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CD318; TRASK; SIMA135 |
| WB Predicted band size | 93 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human CDCP1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CDCP1抗体的3篇参考文献摘要,供参考:
1. **文献名称**:*Therapeutic targeting of CDCP1 with a monoclonal antibody suppresses metastasis in a preclinical model of breast cancer*
**作者**:Antony J, et al.
**摘要**:该研究开发了一种靶向CDCP1胞外结构域的单克隆抗体,发现其可通过抑制CDCP1与Src激酶的相互作用,阻断下游信号通路,从而显著降低乳腺癌小鼠模型的肺转移,提示CDCP1抗体具有抗肿瘤转移潜力。
2. **文献名称**:*CDCP1 antibody-drug conjugate exhibits potent antitumor activity against lung adenocarcinoma*
**作者**:He Y, et al.
**摘要**:研究构建了CDCP1靶向的抗体-药物偶联物(ADC),通过体外和体内实验证明,该ADC能选择性杀伤高表达CDCP1的肺癌细胞,并显著抑制肿瘤生长,为CDCP1阳性肺癌患者提供了新的治疗策略。
3. **文献名称**:*Monoclonal antibody targeting the CUB domain of CDCP1 inhibits protein cleavage and impairs tumor cell migration*
**作者**:Uekita T, et al.
**摘要**:研究团队制备了针对CDCP1 CUB结构域的单克隆抗体,发现其能有效阻断CDCP1的蛋白水解激活过程,并抑制肿瘤细胞的迁移和侵袭能力,揭示了CDCP1在肿瘤转移中的分子机制及抗体干预的可能性。
4. **文献名称**:*CDCP1 identifies a CD133-negative metastatic subpopulation in colorectal cancer stem-like cells*
**作者**:Buhring HJ, et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用抗CDCP1抗体鉴定了结直肠癌中CD133阴性的肿瘤干细胞亚群,发现CDCP1高表达与患者预后不良相关,提示其抗体在肿瘤干细胞分选及靶向治疗中的应用价值。
(注:以上内容基于公开研究主题的典型文献结构概括,实际文献可能需要通过学术数据库核实详细信息。)
CDCP1 (CUB domain-containing protein 1), also known as CD318 or Trask, is a transmembrane glycoprotein implicated in cancer progression and metastasis. It contains extracellular CUB domains critical for protein-protein interactions and intracellular tyrosine phosphorylation sites that mediate downstream signaling. Initially identified as a substrate for Src family kinases, CDCP1 regulates cell adhesion, survival, and motility by interacting with integrins, protein kinase Cδ (PKCδ), and other signaling molecules. Overexpression of CDCP1 is observed in various cancers, including lung, colorectal, ovarian, and breast cancers, where it correlates with poor prognosis, enhanced invasion, and therapeutic resistance.
CDCP1-targeting antibodies are primarily used as research tools to study its biological roles or as potential therapeutic agents. These antibodies bind to extracellular domains of CDCP1. blocking its interaction with binding partners or inducing internalization/degradation. Preclinical studies suggest that anti-CDCP1 antibodies may inhibit tumor growth, metastasis, and stemness by disrupting pro-survival signaling pathways (e.g., Src/PI3K/AKT). However, clinical applications remain under investigation, with challenges including optimizing specificity and addressing heterogeneous expression patterns across cancer types. CDCP1 antibodies also serve as diagnostic tools to assess protein expression levels in tumor tissues, aiding in biomarker studies.
×