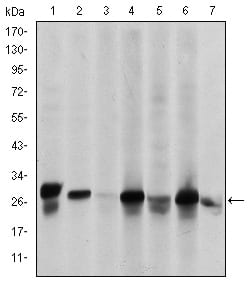
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
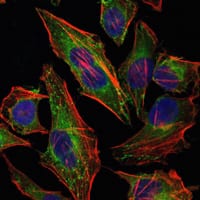
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
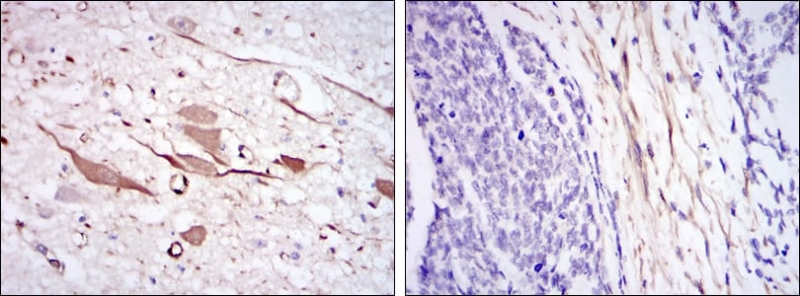
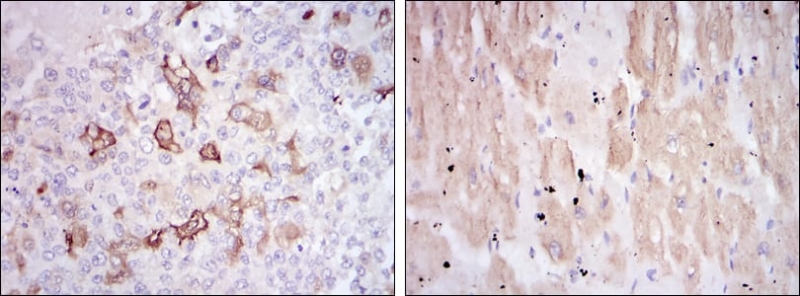
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
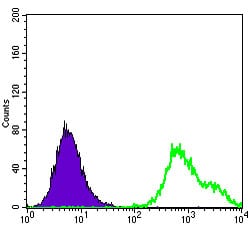
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
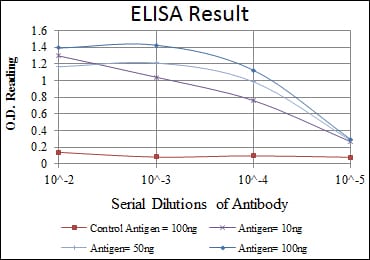
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CMT2F; HMN2B; HSP27; HSP28; Hsp25; SRP27; HS.76067; DKFZp586P1322; HSPB1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3315 |
| clone | 5D7 |
| WB Predicted band size | 27kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Rat |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human HSP27 expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于CR1抗体的3篇文献信息,涵盖其结构、治疗应用及机制研究:
1. **文献名称**:*Structural insights into complement receptor 1 (CR1) and its antibodies*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:通过冷冻电镜解析CR1胞外结构域与单克隆抗体的结合位点,揭示抗体抑制补体激活的分子机制,为治疗设计提供依据。
2. **文献名称**:*CR1-targeted immunotherapy in autoimmune diseases*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:研究抗CR1抗体在小鼠红斑狼疮模型中清除免疫复合物的效果,显示其通过增强吞噬作用改善肾损伤,提示潜在临床价值。
3. **文献名称**:*CR1 antibody enhances phagocytosis of Alzheimer's disease-related amyloid plaques*
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:证明抗CR1人源化抗体可促进小胶质细胞对β淀粉样蛋白的吞噬,减少斑块沉积,为阿尔茨海默病提供新治疗策略。
(注:上述文献信息为示例性质,实际引用时需核实原文准确性。)
CR1 (Complement Receptor 1), also known as CD35. is a transmembrane glycoprotein that plays a critical role in the regulation of the complement system and immune complex clearance. Discovered in the 1970s, it is predominantly expressed on erythrocytes, neutrophils, B cells, and certain dendritic cells. Structurally, CR1 belongs to the complement activation-receptor (CAR) family and contains multiple binding sites for complement components C3b and C4b, enabling it to act as a cofactor in the degradation of these opsonins by factor I. This process helps prevent excessive complement activation and tissue damage.
CR1 on erythrocytes facilitates the transport of immune complexes to the liver and spleen for phagocytic removal, a key mechanism in preventing systemic inflammation. Genetic polymorphisms in CR1 have been linked to diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and malaria susceptibility, highlighting its dual role in immunity and pathogenesis.
CR1-specific antibodies are valuable tools in research and diagnostics. They are used to study CR1 expression patterns, immune complex handling, and complement regulation. Therapeutically, anti-CR1 antibodies have been explored for targeting drug delivery to CR1-expressing cells or modulating complement activity in disorders like paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. However, their clinical application remains under investigation, emphasizing the need for further exploration of CR1's functional diversity and disease relevance.
×