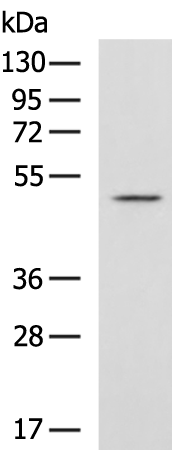
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | TAT; MEC17; C6orf134; Nbla00487; alpha-TAT; alpha-TAT1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 47 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human ATAT1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于ATAT1抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要内容的简要总结:
1. **文献名称**:*α-Tubulin Acetylation by ATAT1 Modulates Microtubule Dynamics and Function*
**作者**:Akella, J.S., et al.
**摘要**:该研究鉴定了ATAT1作为主要的α-微管蛋白乙酰转移酶,通过抗体检测发现其乙酰化修饰增强了微管的稳定性和机械性能,影响纤毛形成和细胞迁移。
2. **文献名称**:*ATAT1-mediated acetylation of α-tubulin directs neuronal motility and axon regeneration*
**作者**:Kalebic, N., et al.
**摘要**:利用ATAT1特异性抗体,研究揭示了神经元中微管乙酰化通过调控微管动力学促进轴突再生,ATAT1缺失导致小鼠神经元迁移和损伤修复能力下降。
3. **文献名称**:*Loss of α-tubulin acetylation impairs human dendritic cell activation and T cell responses*
**作者**:Shida, T., et al.
**摘要**:通过ATAT1抗体阻断实验,证明树突状细胞中微管乙酰化缺失会削弱免疫突触形成,导致T细胞活化效率降低,提示ATAT1在免疫应答中的关键作用。
4. **文献名称**:*ATAT1 controls cilium stability and regulates Hedgehog signaling in development*
**作者**:Ohkawa, K., et al.
**摘要**:研究利用ATAT1敲除模型及抗体染色,发现纤毛微管乙酰化水平下降导致Hedgehog信号通路异常,影响胚胎发育中的组织模式形成。
这些文献均通过ATAT1抗体验证了其在微管修饰及细胞功能中的核心作用,涵盖细胞动力学、神经发育及免疫调控等领域。
The ATAT1 antibody is designed to detect α-tubulin acetyltransferase 1 (ATAT1), also known as α-TAT1 or MEC-17. a key enzyme responsible for acetylating α-tubulin at lysine 40 (K40) in microtubules. Discovered in 2006. ATAT1 catalyzes the transfer of acetyl groups to α-tubulin, a post-translational modification critical for regulating microtubule stability, flexibility, and interactions with motor proteins. This acetylation enhances microtubule resilience against mechanical stress and influences cellular processes such as intracellular transport, cell motility, and cilia formation.
ATAT1 antibodies are widely used in research to study microtubule dynamics, neuronal development, and diseases linked to microtubule dysfunction, including neurodegenerative disorders (e.g., Alzheimer’s) and cancer. They enable detection of acetylated α-tubulin via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry, helping correlate acetylation levels with cellular states or therapeutic responses. Notably, reduced ATAT1 activity is associated with impaired axonal transport and ciliopathies, while its overexpression may influence cancer metastasis.
These antibodies also aid in exploring the interplay between acetylation and other post-translational modifications, as well as evaluating HDAC6 inhibitor efficacy in restoring microtubule acetylation. Their specificity for the K40 site makes them vital tools for dissecting ATAT1’s role in cellular physiology and pathology.
×