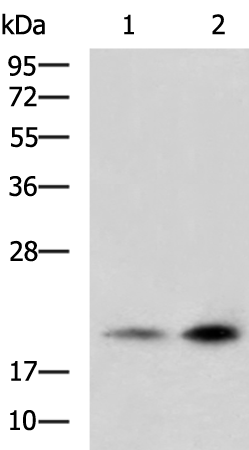
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | AIM; EA1; MLR-3; CLEC2C; GP32/28; BL-AC/P26 |
| WB Predicted band size | 23 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human CD69 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与CD69抗体相关的参考文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**: *CD69 is an immunoregulatory molecule induced following activation*
**作者**: Cebrian, M., et al.
**摘要**: 该研究探讨了CD69作为T细胞早期激活标志物的功能,利用特异性抗体证实其在细胞膜上的表达与淋巴细胞活化的信号传导相关,并提示其可能参与免疫反馈调节。
2. **文献名称**: *CD69 targeting differentially affects the course of collagen-induced arthritis*
**作者**: Sancho, D., et al.
**摘要**: 通过使用抗CD69抗体阻断实验,研究显示CD69在自身免疫性疾病(如类风湿性关节炎)中具有双重作用,既能抑制炎症初期T细胞迁移,又可能加剧慢性炎症阶段的病理损伤。
3. **文献名称**: *CD69 negatively regulates the interaction of α4β1 integrin with fibronectin*
**作者**: López-Cabrera, M., et al.
**摘要**: 利用功能阻断性CD69抗体,揭示了CD69通过调控α4β1整合素与细胞外基质的相互作用,影响淋巴细胞黏附和迁移,提示其在炎症微环境中的动态调节机制。
---
以上文献均聚焦CD69抗体在功能研究中的应用,涵盖免疫激活、自身免疫病机制及细胞迁移调控等领域。如需具体发表年份或期刊信息,可进一步补充检索。
CD69. a transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the C-type lectin receptor family, is an early activation marker expressed on immune cells, including T cells, B cells, natural killer (NK) cells, and monocytes. Discovered in the 1980s, it is encoded by the *CD69* gene and plays a role in regulating immune responses by modulating cell migration, cytokine production, and effector functions. CD69 expression is rapidly induced upon antigen recognition or stimulation, making it a valuable biomarker for identifying activated immune cells in research and clinical settings.
CD69 antibodies are essential tools for detecting and characterizing activated immune cell populations. In flow cytometry, they help distinguish recently activated lymphocytes from resting cells, aiding studies on immune activation dynamics in infections, autoimmune diseases, and cancer. Additionally, CD69 antibodies are used in functional assays to investigate its signaling pathways, including interactions with ligands like S1PR1. which influence lymphocyte retention in lymphoid organs.
Therapeutic interest in CD69 has grown due to its regulatory roles in inflammation and immune tolerance. Blocking CD69 with monoclonal antibodies has shown potential in preclinical models to ameliorate autoimmune conditions or enhance anti-tumor immunity. Conversely, agonistic antibodies might suppress excessive inflammation. Despite promising findings, clinical applications remain exploratory, with ongoing research focused on optimizing specificity and understanding context-dependent effects. CD69 antibodies thus serve as both diagnostic reagents and investigational agents bridging basic immunology and translational medicine.
×