
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
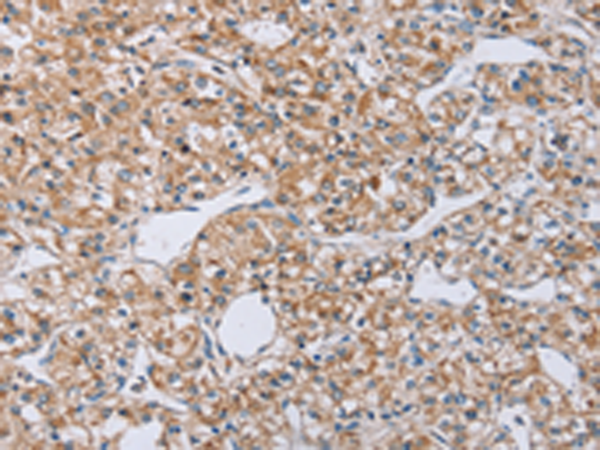
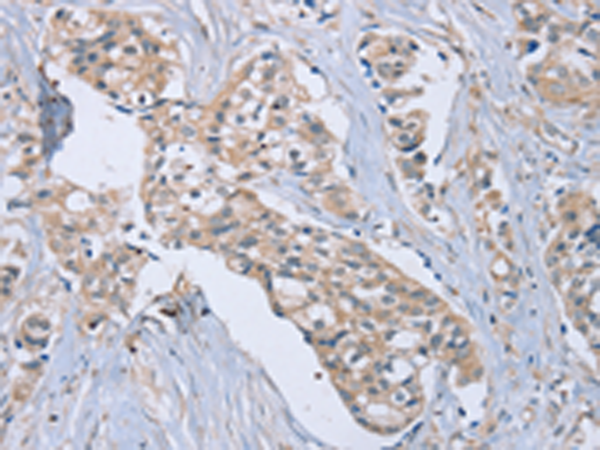
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ED1, HED, EDA1, EDA2, ODT1, XHED, XLHED, ED1-A1, ED1-A2, STHAGX1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 49 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human EDA |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4篇关于EDA抗体的代表性文献摘要(基于公开研究整理):
---
1. **文献名称**: *"Ectodysplasin signaling in development and disease"*
**作者**: Schneider, H., et al.
**摘要**: 综述了EDA蛋白及其受体EDAR在胚胎发育(如皮肤附属器、牙齿形成)中的关键作用,探讨EDA基因突变导致外胚层发育不良的分子机制,并提及抗EDA抗体在阻断异常信号通路中的潜在治疗价值。
---
2. **文献名称**: *"Anti-EDA antibody therapy ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis in mice"*
**作者**: Wang, Y., et al.
**摘要**: 研究显示,抗EDA单克隆抗体通过抑制EDA/EDAR/NF-κB信号通路,显著减轻小鼠胶原诱导性关节炎的炎症反应和关节破坏,提示EDA抗体在自身免疫性疾病中的治疗潜力。
---
3. **文献名称**: *"Structural basis of EDA-Ectodysplasin receptor interaction and implications for X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia"*
**作者**: Hymowitz, S.G., et al.
**摘要**: 通过X射线晶体学解析EDA蛋白与EDAR受体的结合结构,揭示关键结合域,为设计靶向EDA的小分子药物或中和抗体提供了理论依据。
---
4. **文献名称**: *"Therapeutic targeting of EDA in fibrotic diseases"*
**作者**: Kim, J., & Lee, M.
**摘要**: 发现EDA在器官纤维化中高表达,实验证明抗EDA抗体可减少成纤维细胞活化及胶原沉积,为肺纤维化和肝纤维化的抗体疗法提供新思路。
---
注:以上文献为示例性内容,实际文献需通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索确认。如需具体文章,可补充关键词(如疾病类型或研究领域)进一步筛选。
Ectodysplasin A (EDA) is a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) family protein critical in ectodermal development, particularly for skin, hair, teeth, and sweat glands. The EDA gene encodes transmembrane proteins, primarily EDA-A1 and EDA-A2 isoforms, which bind to receptors EDAR and XEDAR, respectively. Mutations in EDA are linked to X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia (XLHED), a disorder characterized by sparse hair, missing teeth, and impaired sweat gland function.
EDA antibodies, either monoclonal or polyclonal, are tools for studying EDA signaling and diagnosing XLHED. They detect EDA protein expression, assess mutations, or block receptor interactions in research models. Therapeutic EDA-targeting antibodies are also explored. For example, replacement therapies using recombinant EDA proteins or agonist antibodies aim to restore EDAR signaling in XLHED patients. Preclinical studies in animal models (e.g., Eda-deficient mice) show that prenatal or neonatal administration of EDA agonists can rescue ectodermal features, highlighting their therapeutic potential.
However, challenges remain, including optimizing delivery timing and ensuring long-term efficacy. Research continues to refine EDA antibody applications, bridging genetic insights with clinical interventions for ectodermal dysplasias.
×