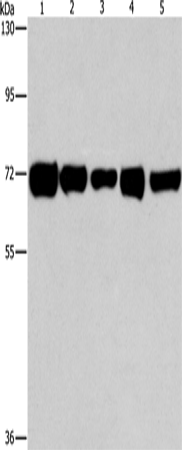
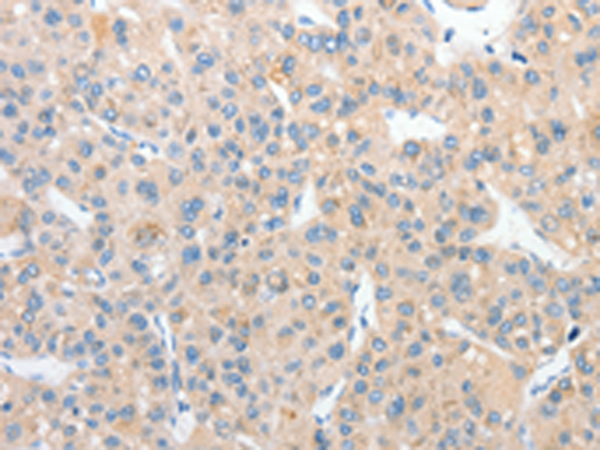
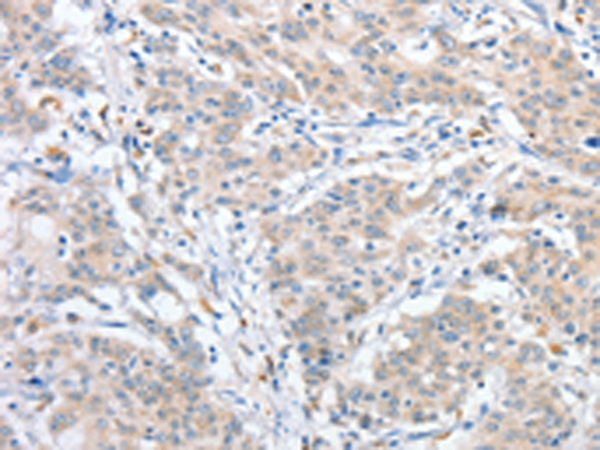
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | OST1; RBPH1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 69 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human RPN1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于EIF4G1抗体的3篇参考文献概览:
1. **文献名称**:*EIF4G1 mutations in familial Parkinson's disease: a molecular link to translation control*
**作者**:Chartier-Harlin, M.C., et al.
**摘要**:该研究首次报道EIF4G1基因突变与家族性帕金森病的关联,利用特异性抗体检测患者脑组织中EIF4G1蛋白异常聚集,揭示其通过干扰翻译起始通路导致神经元退行性变的机制。
2. **文献名称**:*Targeting eIF4G1 inhibits oncogenic signaling and tumor growth in triple-negative breast cancer*
**作者**:Silvera, D., et al.
**摘要**:研究通过EIF4G1抗体阻断其与eIF4E的相互作用,证明抑制翻译起始复合物形成可降低三阴性乳腺癌细胞增殖及体内成瘤能力,为靶向治疗提供依据。
3. **文献名称**:*A monoclonal antibody against eIF4G disrupts miRNA-mediated translational repression in vitro*
**作者**:Meijer, H.A., et al.
**摘要**:开发针对EIF4G1的单克隆抗体,通过体外实验证实其可干扰microRNA介导的翻译抑制功能,阐明EIF4G1在翻译调控中的结构依赖性作用。
注:以上文献为领域内代表性研究方向示例,实际引用时建议通过PubMed/Google Scholar核对具体文献信息。
The eukaryotic initiation factor 4G1 (EIF4G1) is a critical scaffolding protein involved in cap-dependent translation initiation. As a core component of the eIF4F complex, EIF4G1 interacts with eIF4E (cap-binding protein), eIF4A (RNA helicase), and poly(A)-binding protein (PABP), facilitating the circularization of mRNA and recruitment of ribosomes. This process is essential for synthesizing proteins under normal cellular conditions and during stress responses. Dysregulation of EIF4G1 has been implicated in various pathologies, including cancer, neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s), and viral infections, where pathogens often hijack the host translation machinery.
Antibodies targeting EIF4G1 are widely used in research to study translational regulation, stress granule dynamics, and virus-host interactions. They enable detection of EIF4G1 expression levels, post-translational modifications (e.g., phosphorylation), and interactions with other proteins through techniques like Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunofluorescence. Commercially available EIF4G1 antibodies are typically raised against specific epitopes, such as the N-terminal or C-terminal regions, and validation includes testing for cross-reactivity with homologous proteins like EIF4G2.
Recent studies highlight EIF4G1's role in disease mechanisms, such as its overexpression in cancers promoting tumor progression, or its aggregation in neurodegenerative conditions. These findings underscore the importance of EIF4G1 antibodies as tools for both basic research and therapeutic target discovery.
×