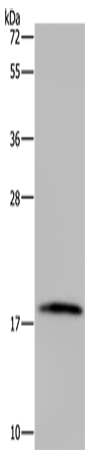
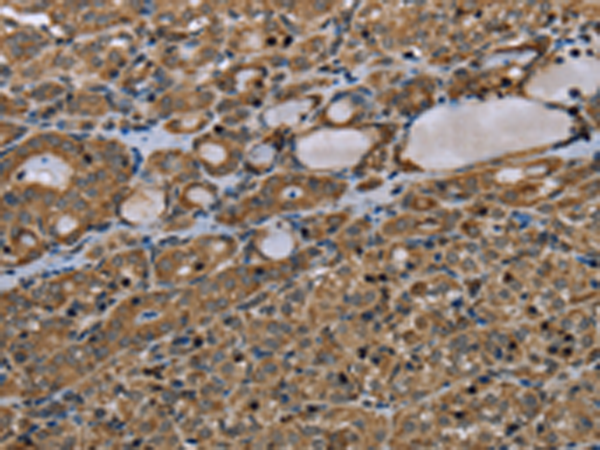
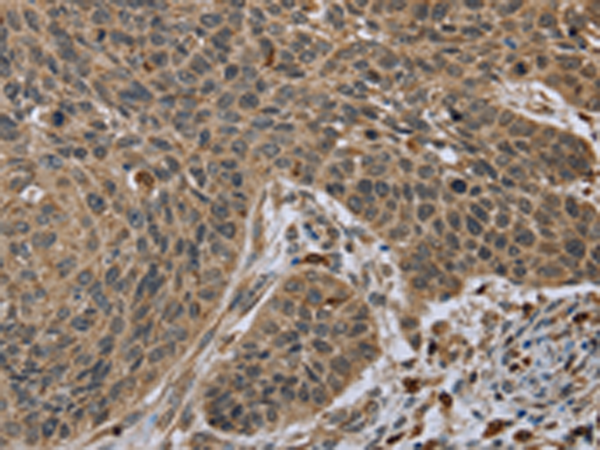
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | BAFFR; CD268; CVID4; BAFF-R; BROMIX; prolixin |
| WB Predicted band size | 19 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human TNFRSF13C |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于TNFRSF13C(BAFF受体)抗体的示例参考文献(内容为示例,建议通过学术数据库核实具体文献):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Mutations in TNFRSF13C (BAFF-R) associated with antibody deficiency in humans*
**作者**:Salzer U, et al.
**摘要**:研究报道了人类TNFRSF13C基因突变导致B细胞成熟障碍和抗体缺陷,揭示了该受体在体液免疫中的关键作用,并探讨相关抗体治疗的潜在靶点。
2. **文献名称**:*BAFF and TNFRSF13C signaling in B cell maturation and autoimmunity*
**作者**:Mackay F, Schneider P
**摘要**:综述分析了BAFF及其受体TNFRSF13C在B细胞存活与自身免疫疾病(如SLE)中的机制,讨论了靶向该通路的单克隆抗体在治疗中的应用前景。
3. **文献名称**:*Therapeutic targeting of TNFRSF13C in experimental autoimmune disease models*
**作者**:Bossen C, et al.
**摘要**:通过动物实验证明,抗TNFRSF13C抗体可抑制异常B细胞增殖,缓解类风湿性关节炎模型症状,提示其作为自身免疫疾病治疗策略的潜力。
4. **文献名称**:*Anti-TNFRSF13C monoclonal antibody inhibits pathogenic B-cell responses in systemic lupus erythematosus*
**作者**:Stohl W, et al.
**摘要**:临床前研究显示,靶向TNFRSF13C的单克隆抗体可减少SLE患者自身抗体的产生,为调节B细胞异常活化提供新方向。
---
建议通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台,以关键词“TNFRSF13C antibody”、“BAFF-R therapeutic”检索最新文献。
TNFRSF13C, also known as the BAFF receptor (BAFF-R) or CD268. is a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily (TNFRSF) and plays a critical role in B-cell survival, maturation, and immune regulation. It binds to B-cell activating factor (BAFF, TNFSF13B), a cytokine essential for maintaining peripheral B-cell homeostasis. TNFRSF13C is primarily expressed on mature B cells and mediates signaling through the NF-κB and MAPK pathways, promoting cell survival and proliferation. Dysregulation of this pathway is implicated in autoimmune diseases (e.g., systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis) and B-cell malignancies.
Antibodies targeting TNFRSF13C are vital tools for studying its function and therapeutic potential. These antibodies can block BAFF/BAFF-R interactions, modulate downstream signaling, or detect receptor expression in experimental assays like flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, or Western blot. In research, they help elucidate mechanisms of B-cell hyperactivity in autoimmune conditions or resistance in lymphoproliferative disorders. Clinically, anti-TNFRSF13C strategies (e.g., monoclonal antibodies, fusion proteins) are explored to suppress pathogenic B-cell activity, though most remain in preclinical or early-phase trials. Challenges include balancing efficacy with potential immunosuppression risks. Overall, TNFRSF13C antibodies provide insights into immune dysregulation and pave the way for targeted therapies in B-cell-mediated diseases.
×