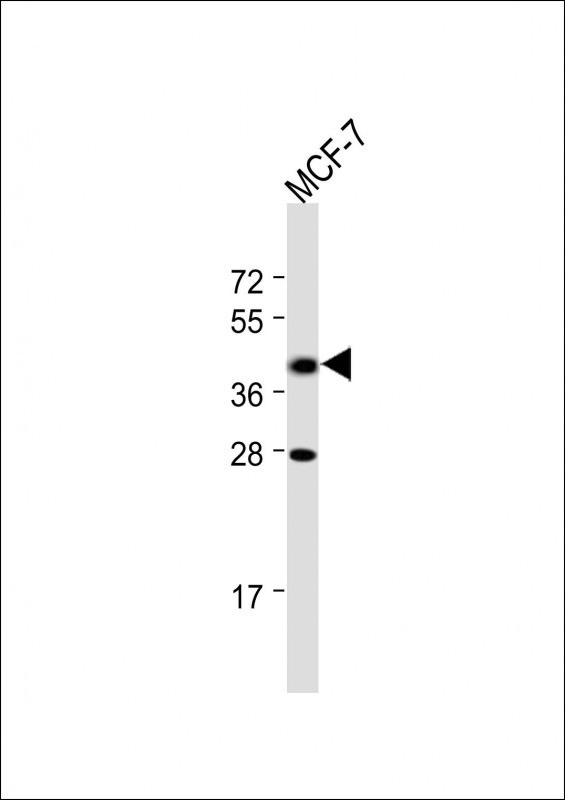
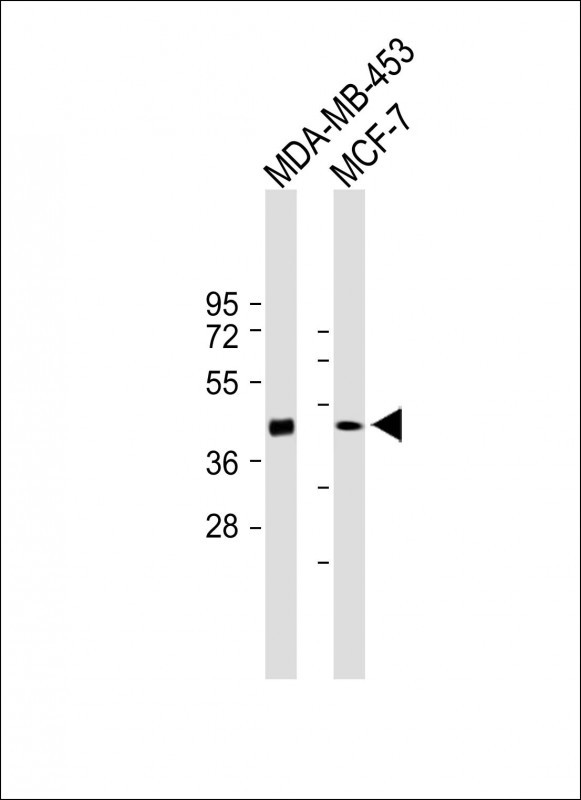
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Major histocompatibility complex class I-related gene protein, MHC class I-related gene protein, Class I histocompatibility antigen-like protein, MR1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3140 |
| WB Predicted band size | 39.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This MR1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 312-341 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human MR1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于MR1抗体的3篇参考文献概览:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"A conserved human T cell population targets MHC class I-related molecule MR1"*
**作者**:Le Bourhis L. et al.
**摘要**:该研究首次报道了MR1限制性T细胞(如MAIT细胞)的功能,并通过特异性抗体证实MR1在抗原呈递中的关键作用,揭示了其在微生物免疫应答中的保守性。
---
2. **文献名称**:*"Antibody-mediated targeting of MR1 dampens macrophage activation"*
**作者**:McWilliam H.E.G. et al.
**摘要**:研究团队开发了一种靶向MR1的单克隆抗体,证明其可抑制MR1与代谢产物结合,从而降低巨噬细胞的炎症反应,为自身免疫疾病治疗提供新策略。
---
3. **文献名称**:*"Structural insight into MR1-mediated antigen presentation"*
**作者**:Gherardin N.A. et al.
**摘要**:通过冷冻电镜和抗体阻断实验,解析了MR1分子与配体及T细胞受体的互作机制,阐明了其抗原呈递的结构基础,为设计靶向MR1的免疫疗法奠定基础。
---
如需具体研究细节,建议通过PubMed或期刊官网检索完整文献。
**Background of MR1 Antibodies**
MR1 (MHC class I-related molecule) is a highly conserved antigen-presenting molecule that plays a unique role in immune surveillance. Unlike classical MHC-I molecules, MR1 presents microbial metabolites, particularly vitamin B2 (riboflavin) and B9 (folate) derivatives, to mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells. These metabolites, derived from bacteria or fungi, are captured by MR1 and presented on the cell surface, enabling MAIT cells to detect and respond to infections.
MR1 antibodies are tools designed to target this MR1-antigen complex or the MR1 molecule itself. They have become critical in studying MR1’s immunobiology, including its structural interactions with antigens and T-cell receptors (TCRs). For example, monoclonal antibodies like 26.5 and 8F04.F9 can block MR1-antigen presentation or stabilize MR1 conformations, aiding in mechanistic studies.
Clinically, MR1 antibodies hold therapeutic potential. By modulating MR1-mediated immune responses, they may enhance anti-infection or anti-tumor immunity. MAIT cells, activated via MR1. exhibit dual roles in diseases—protective in infections but potentially harmful in autoimmunity or chronic inflammation. MR1-targeting antibodies could thus fine-tune these responses.
Research also explores MR1’s role in cancer, as some tumors overexpress MR1. Antibodies like MR1m1 are being tested to redirect T cells against MR1-positive malignancies. Overall, MR1 antibodies bridge fundamental immunology and translational applications, offering insights into microbial immunity and novel therapeutic strategies.
×