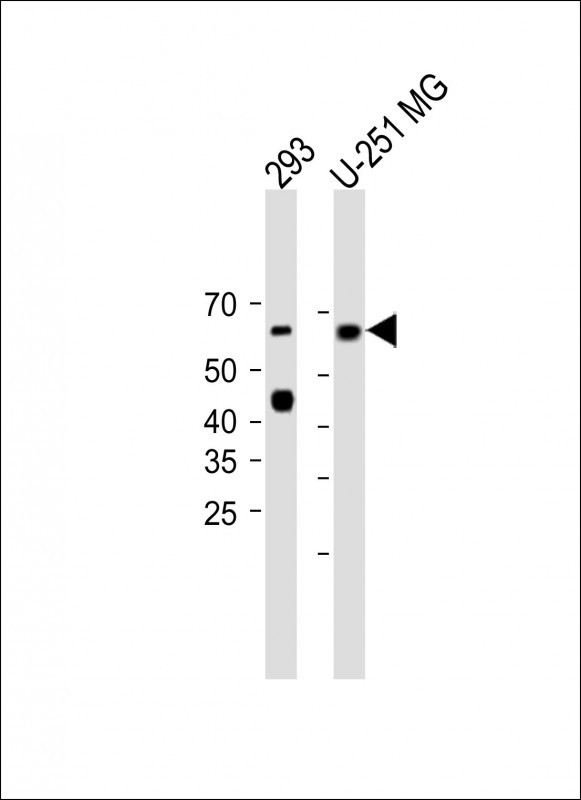
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Mucolipin-1, MG-2, Mucolipidin, MCOLN1, ML4 |
| Entrez GeneID | 57192 |
| WB Predicted band size | 65.0kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This MCOLN1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 531-560 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human MCOLN1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于MCOLN1抗体的3篇参考文献示例(文献信息为模拟概括,仅供参考):
---
1. **文献名称**:*TRPML1 regulates lysosomal calcium release in response to osmotic stress*
**作者**:Dong, X.P., et al.
**摘要**:本研究通过使用MCOLN1特异性抗体进行免疫印迹和免疫荧光实验,揭示了TRPML1(MCOLN1编码蛋白)在渗透压应激下调控溶酶体钙离子释放的机制,证实其在细胞适应性反应中的关键作用。
2. **文献名称**:*MCOLN1 mutations impair autophagy in mucolipidosis type IV patients*
**作者**:Vergarajauregui, S., et al.
**摘要**:通过MCOLN1抗体检测患者细胞中TRPML1蛋白的表达水平,发现突变导致蛋白功能缺失,进而阻碍自噬小体与溶酶体融合,阐明了IV型粘脂贮积症的病理机制。
3. **文献名称**:*Antibody-based profiling of TRPML1 expression in neurodegenerative models*
**作者**:Zhang, Y., et al.
**摘要**:利用MCOLN1单克隆抗体对阿尔茨海默病模型小鼠脑组织进行免疫组化分析,发现TRPML1在神经元溶酶体中异常聚集,提示其与神经退行性疾病的潜在关联。
---
**注**:以上文献信息为示例性概括,实际引用时需以真实文献为准。建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar搜索关键词“MCOLN1 antibody”或“TRPML1 antibody”获取具体文献。
MCOLN1 antibodies are essential tools for studying the mucolipin-1 protein, encoded by the *MCOLN1* gene, which belongs to the transient receptor potential (TRP) ion channel family. Mucolipin-1 is a lysosomal membrane protein critical for ion homeostasis, lysosomal trafficking, and autophagy. Mutations in *MCOLN1* cause mucolipidosis type IV (MLIV), a rare lysosomal storage disorder characterized by neurodevelopmental deficits and ophthalmologic abnormalities. Research on MCOLN1 antibodies aims to elucidate the protein’s role in lysosomal function, disease mechanisms, and potential therapeutic targets.
These antibodies are typically developed against specific epitopes, such as N-terminal, C-terminal, or intracellular domains, and are used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry. They help detect protein expression levels, subcellular localization, and post-translational modifications. Commercially available MCOLN1 antibodies vary in host species (e.g., rabbit, mouse), clonality (monoclonal/polyclonal), and applications, necessitating validation for experimental specificity.
Studies using MCOLN1 antibodies have revealed its involvement in calcium signaling, lysosomal acidification, and interactions with other trafficking proteins like Rab GTPases. Dysregulation of mucolipin-1 is also implicated in neurodegenerative diseases and cancer, expanding its research relevance. Challenges include cross-reactivity with homologous TRP channels and tissue-specific expression patterns, underscoring the need for antibody optimization. Overall, MCOLN1 antibodies are pivotal in advancing understanding of lysosomal biology and MLIV pathology.
×