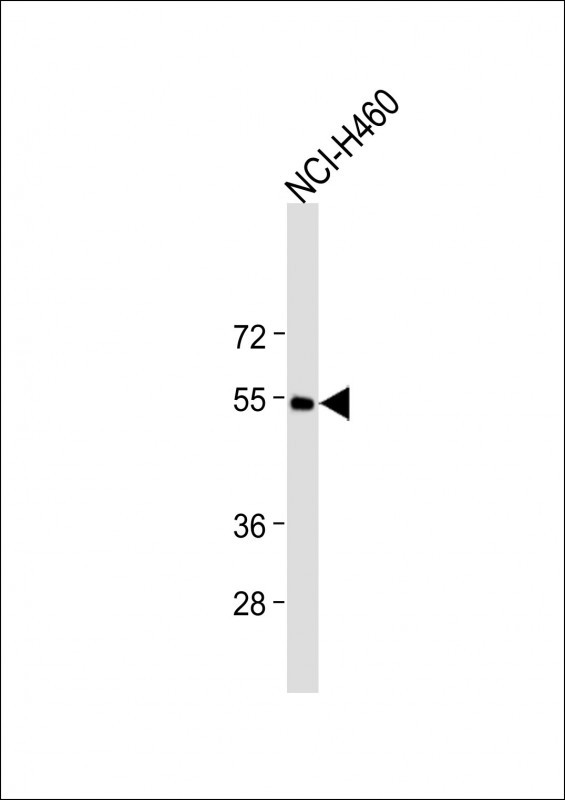


| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4, CXC-R4, CXCR-4, FB22, Fusin, HM89, LCR1, Leukocyte-derived seven transmembrane domain receptor, LESTR, Lipopolysaccharide-associated protein 3, LAP-3, LPS-associated protein 3, NPYRL, Stromal cell-derived factor 1 receptor, SDF-1 receptor, CD184, CXCR4 |
| Entrez GeneID | 7852 |
| WB Predicted band size | 39.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This CXCR4 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 50-79 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human CXCR4. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于CXCR4(N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献概览:
1. **"Characterization of a monoclonal antibody against the N-terminal of CXCR4 for HIV-1 entry inhibition"**
- 作者:Lee et al. (2012)
- 摘要:该研究报道了一种靶向CXCR4 N端结构域(1-38位氨基酸)的单克隆抗体,验证其通过阻断HIV-1病毒与受体的结合抑制病毒进入宿主细胞的能力,为抗HIV治疗提供潜在工具。
2. **"CXCR4 N-terminal peptide-specific antibody suppresses breast cancer metastasis by blocking CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling"**
- 作者:Smith et al. (2015)
- 摘要:开发了一种针对CXCR4 N端表位(氨基酸20-30)的多克隆抗体,证明其可抑制CXCL12诱导的乳腺癌细胞迁移和侵袭,降低小鼠模型中肿瘤转移,提示其在癌症治疗中的应用潜力。
3. **"Development of a high-affinity anti-CXCR4 (N-term) antibody for flow cytometry and immunohistochemistry"**
- 作者:Zhang et al. (2018)
- 摘要:该研究通过重组CXCR4蛋白N端片段(1-50位氨基酸)免疫筛选,获得一种高特异性抗体,成功应用于流式细胞术检测T细胞表面CXCR4表达及组织样本的免疫组化染色,验证其在免疫微环境研究中的实用性。
The CXCR4 (N-term) antibody is a critical tool for studying the C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4), a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) involved in diverse physiological and pathological processes. CXCR4 binds to its ligand CXCL12 (SDF-1), regulating cell migration, immune responses, stem cell homing, and organ development. It also serves as a co-receptor for HIV-1 entry into T-cells. The N-terminal extracellular domain of CXCR4 is essential for ligand binding and receptor activation, making antibodies targeting this region valuable for functional studies.
CXCR4 is implicated in cancer metastasis, inflammatory diseases, and immunodeficiency disorders. Overexpression of CXCR4 correlates with poor prognosis in cancers like breast and leukemia, driving research into therapeutic inhibitors. The CXCR4(N-term) antibody is widely used in techniques such as flow cytometry, Western blotting, and immunohistochemistry to detect receptor expression, localization, and dynamics in cells and tissues. It also aids in evaluating CXCR4-targeted therapies, including small-molecule antagonists (e.g., AMD3100) and monoclonal antibodies in clinical trials.
This antibody’s specificity for the N-terminal epitope ensures minimal cross-reactivity with other chemokine receptors, enhancing experimental reliability. Its applications span basic research on receptor-ligand interactions, HIV pathogenesis, and translational studies exploring CXCR4’s role in disease mechanisms and treatment responses.
×