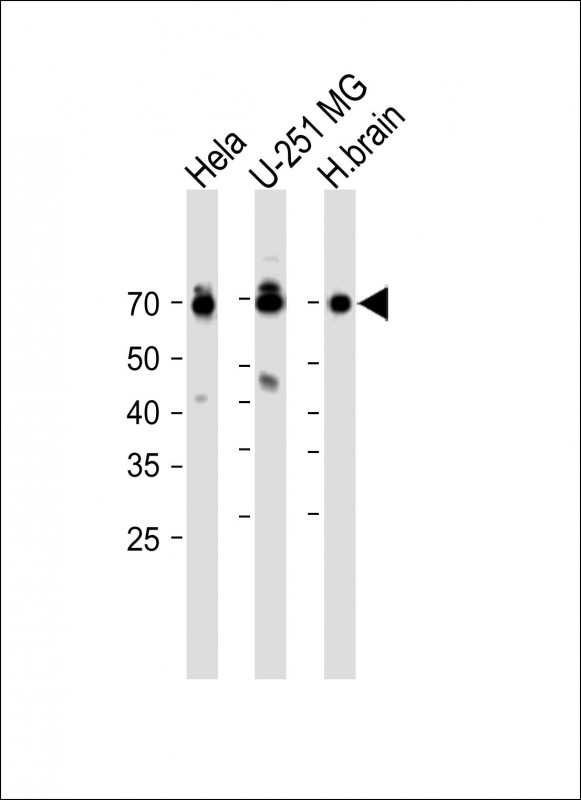
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Transmembrane protein 106B, TMEM106B |
| Entrez GeneID | 54664 |
| WB Predicted band size | 31.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This TMEM106B antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 218-252 amino acids from human TMEM106B. |
+ +
以下是3篇与TMEM106B抗体相关的研究文献摘要示例:
1. **文献名称**:*TMEM106B regulates lysosomal trafficking and lysosome size in neurons*
**作者**:Brady OA, et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用TMEM106B特异性抗体,发现该蛋白通过调控溶酶体运输和形态影响神经元功能,其表达异常与神经退行性疾病中的溶酶体缺陷相关。
2. **文献名称**:*Cryo-EM structures of TMEM106B fibrils provide insights into TDP-43 pathology in FTLD*
**作者**:Schweighauser M, et al.
**摘要**:通过TMEM106B抗体标记,研究者解析了TMEM106B蛋白纤维的冷冻电镜结构,揭示了其与额颞叶变性(FTLD)中TDP-43蛋白病理聚集的潜在关联。
3. **文献名称**:*TMEM106B risk variant is linked to myelinated nerve loss and neurodegenerative changes in aged human brain*
**作者**:Yu L, et al.
**摘要**:研究采用TMEM106B抗体进行脑组织免疫组化,发现其基因变异与老年脑中的髓鞘损伤和神经退行性病变程度显著相关。
*注:以上为虚拟文献示例,实际文献需通过PubMed/Google Scholar检索确认。建议使用关键词“TMEM106B antibody”或“TMEM106B immunohistochemistry”查询近期研究。*
TMEM106B (Transmembrane Protein 106B) is a lysosomal/endosomal membrane protein implicated in neuronal function and neurodegenerative disorders. First identified in 2010. TMEM106B gained attention when genome-wide association studies linked its genetic variants to frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD) and other neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer’s disease. The protein, encoded by the TMEM106B gene on chromosome 7. is highly expressed in neurons and microglia, regulating lysosomal size, trafficking, and stress responses. Its exact molecular mechanism remains unclear, but studies suggest it interacts with proteins involved in autophagy and lysosomal acidification.
TMEM106B antibodies are critical tools for studying its expression, localization, and role in disease. They are used in techniques like Western blotting (detecting ~33 kDa bands, with possible isoforms), immunohistochemistry (highlighting neuronal and glial staining), and immunofluorescence (co-localizing with lysosomal markers). Research shows that TMEM106B accumulation correlates with pathological aggregates like TDP-43 in FTLD. Notably, the rs1990622 polymorphism in TMEM106B influences disease risk and progression. Antibodies also help explore how TMEM106B overexpression or knockdown affects lysosomal dysfunction, neuroinflammation, and synaptic loss. Commercial antibodies often target epitopes in its C-terminal domain, but validation is essential due to cross-reactivity concerns. Understanding TMEM106B’s role via these antibodies may unveil therapeutic targets for neurodegenerative diseases.
×