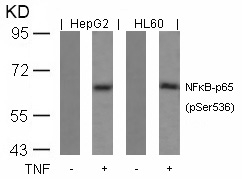
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
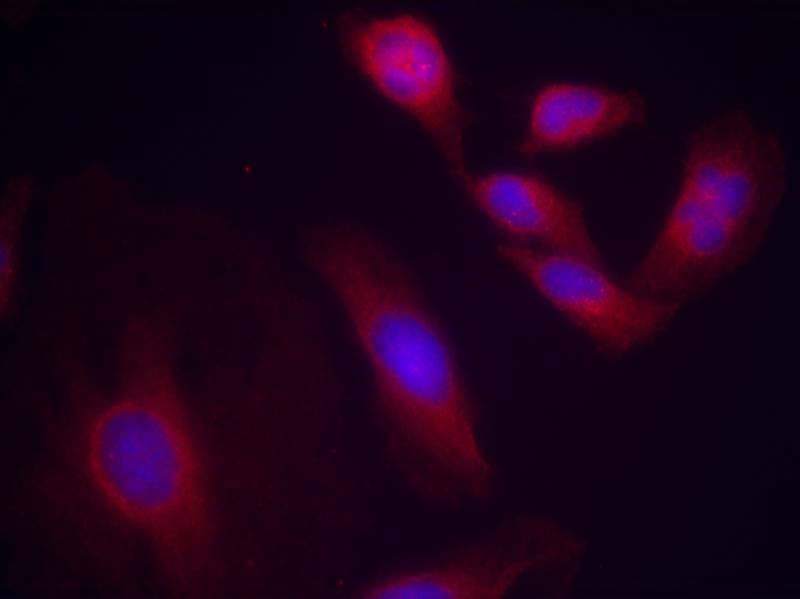
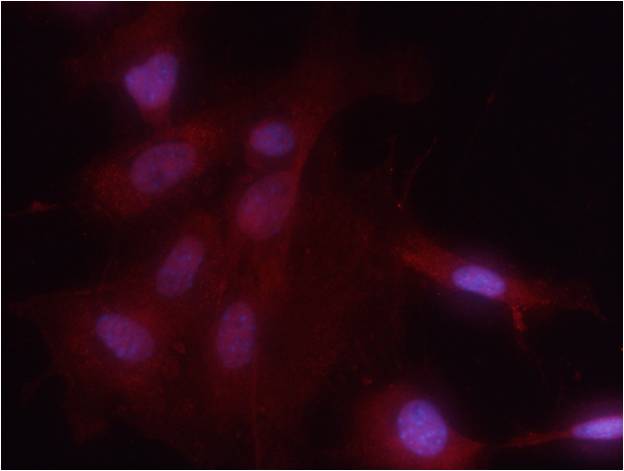
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
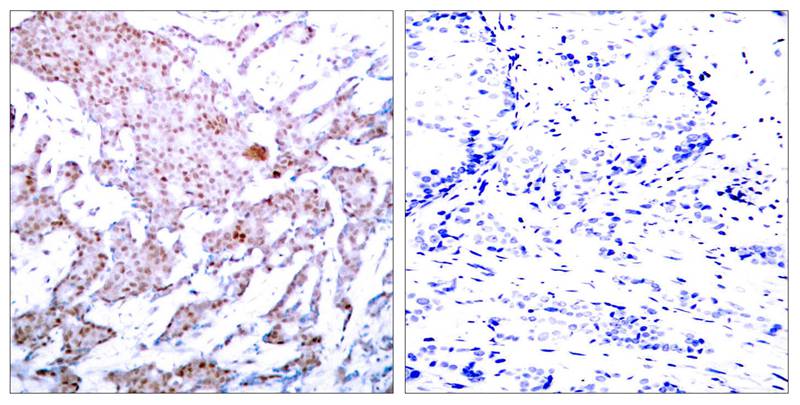
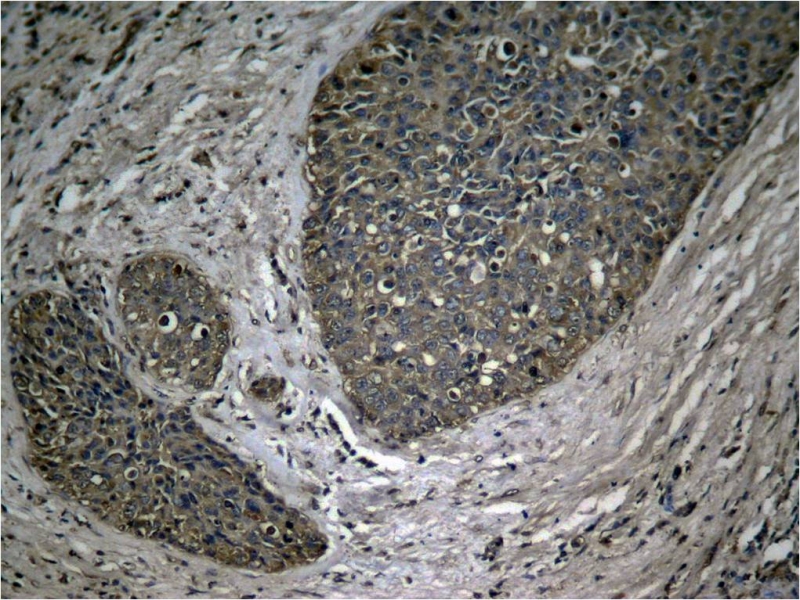
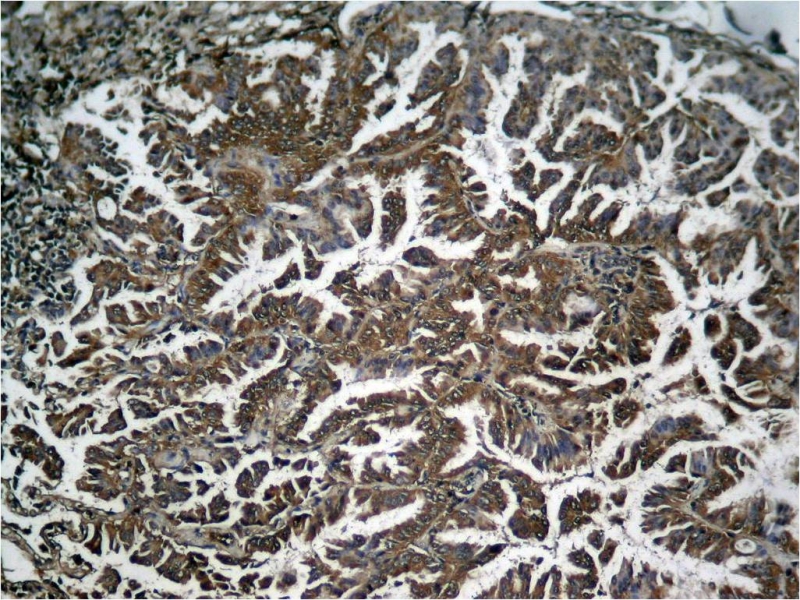
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | NFKB3; RELA; TF65; Transcription factor p65; p65 |
| Entrez GeneID | 5970; |
| WB Predicted band size | 65kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Peptide sequence around phosphorylation site of serine 536 (F-S-S(p)-I-A) derived from Human NFkB-p65. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于NF-κB p65 (Phospho-Ser536)抗体的3篇参考文献,涵盖其在不同研究中的应用:
1. **"NF-κB in development and progression of human cancer"**
- **作者**: Dolcet X, et al. (2005)
- **摘要**: 研究NF-κB在肿瘤发生中的作用,通过Phospho-Ser536抗体检测p65在多种癌症组织中的磷酸化水平,发现其激活与肿瘤侵袭性和不良预后相关。
2. **"TNF-α induces phosphorylation of p65/RelA on serine 536 via IKK-independent pathways"**
- **作者**: Sakurai H, et al. (2003)
- **摘要**: 揭示TNF-α通过非经典IKK途径诱导p65 Ser536磷酸化,使用该抗体验证磷酸化位点,并证明其对NF-κB转录活性的调控作用。
3. **"Selective activation of NF-κB subunits in human breast cancer"**
- **作者**: Buss H, et al. (2004)
- **摘要**: 分析乳腺癌细胞中NF-κB亚基的激活状态,利用Phospho-Ser536抗体发现p65磷酸化与癌细胞存活和化疗耐药性密切相关。
4. **"Phosphorylation of RelA/p65 on serine 536 defines an IκBα-independent NF-κB pathway"**
- **作者**: Yang F, et al. (2003)
- **摘要**: 提出Ser536磷酸化是独立于IκBα降解的NF-κB激活新机制,通过该抗体证实其在LPS刺激巨噬细胞中的关键作用。
这些文献展示了该抗体在癌症机制、炎症信号通路及激酶调控研究中的广泛应用。
The NF-κB-p65 (Phospho-Ser536) antibody is a critical tool for studying the activation status of the NF-κB signaling pathway, which regulates genes involved in inflammation, immunity, cell survival, and stress responses. NF-κB is a transcription factor family, with p65 (RelA) being a major subunit. In resting cells, NF-κB is sequestered in the cytoplasm by inhibitory IκB proteins. Upon stimulation (e.g., cytokines, pathogens, stress), IκB kinases (IKK) phosphorylate IκB, leading to its degradation and subsequent nuclear translocation of NF-κB. Phosphorylation of p65 at Ser536. located in the transactivation domain, is a key post-translational modification that enhances transcriptional activity, promotes nuclear retention, and regulates interactions with coactivators. This phosphorylation event can be mediated by multiple kinases, including IKKβ, RSK1. or mTOR, depending on the stimulus and cellular context.
The NF-κB-p65 (Phospho-Ser536) antibody specifically detects endogenous p65 phosphorylated at Ser536. enabling researchers to assess pathway activation in models of infection, cancer, autoimmune diseases, or neurodegenerative disorders. It is widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry. Aberrant NF-κB activation linked to Ser536 phosphorylation has been implicated in chronic inflammation, tumor progression, and therapy resistance. Validating antibody specificity through knockout controls or phosphatase treatment is essential, as cross-reactivity with other phospho-epitopes or family members may occur. This antibody aids in elucidating mechanisms of NF-κB regulation and evaluating therapeutic interventions targeting this pathway.
×