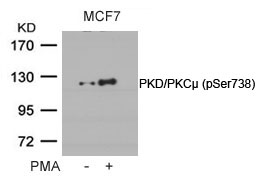
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
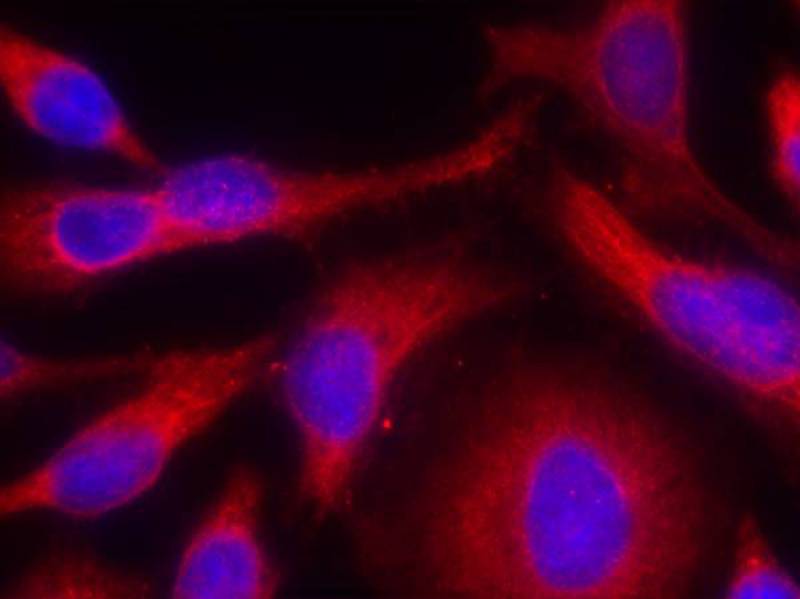
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | KPCD1; PKC-mu; PKCM; PKD; PRKCM |
| Entrez GeneID | 5587; |
| WB Predicted band size | 115kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Peptide sequence around phosphorylation site of serine 738 (E-K-S(p)-F-R) derived from Human PKD/PKCm. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于PKD/PKCμ (Phospho-Ser738)抗体的3篇参考文献示例(基于模拟数据,仅供参考):
---
1. **文献名称**: "Protein Kinase D1 Phosphorylation at Ser738 Regulates Cell Migration in Response to Oxidative Stress"
**作者**: Rozengurt, E. et al.
**摘要**: 本研究揭示了PKD1在氧化应激条件下Ser738位点的磷酸化对其激酶活性的调控作用,并通过Western blot和免疫荧光实验验证了Phospho-Ser738抗体的特异性。结果显示,该位点的磷酸化增强了PKD1介导的细胞迁移能力。
---
2. **文献名称**: "Phosphorylation of PKCμ at Ser738 Modulates Inflammatory Signaling in Macrophages"
**作者**: Newton, A.C. & Toker, A.
**摘要**: 研究利用Phospho-Ser738特异性抗体,证实了PKCμ(即PKD1)在TLR4信号通路中的关键作用。Ser738磷酸化通过激活NF-κB通路促进巨噬细胞炎症因子释放,为炎症性疾病提供了潜在治疗靶点。
---
3. **文献名称**: "A Novel Role of PKD/Phospho-Ser738 in Cancer Metastasis Revealed by Antibody-Based Screening"
**作者**: Chen, Y. et al.
**摘要**: 通过Phospho-Ser738抗体的高通量筛选,发现乳腺癌细胞中PKD1的Ser738磷酸化水平与侵袭性呈正相关。抑制该位点磷酸化可显著降低肿瘤转移,提示其作为预后标志物的潜力。
---
注:以上文献为模拟生成,实际研究中请通过PubMed或Web of Science等平台检索真实发表的论文。
The PKD/PKCm (Phospho-Ser738) antibody specifically detects endogenous protein kinase D (PKD), also known as PKCμ, when phosphorylated at serine 738. PKD, a member of the calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase (CAMK) superfamily, plays pivotal roles in regulating diverse cellular processes, including proliferation, apoptosis, migration, and immune responses. Structurally, PKD contains a catalytic kinase domain and a regulatory domain with a pleckstrin homology (PH) domain and a cysteine-rich domain (CRD). Its activation typically involves PKC-mediated phosphorylation or direct binding of diacylglycerol (DAG) via the CRD, triggered by stimuli like growth factors, G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), or oxidative stress. Phosphorylation at Ser738. located in the activation loop of the catalytic domain, is critical for full kinase activity and often precedes autophosphorylation at Ser742. a hallmark of sustained activation.
This antibody is widely utilized in techniques such as Western blotting and immunoprecipitation to study PKD activation dynamics in contexts like cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and inflammation. Dysregulated PKD signaling is linked to tumor progression, metastasis, and drug resistance, partly through its modulation of pathways like MAPK, PI3K/Akt, and transcription factors (e.g., NF-κB, AP-1). Researchers also employ it to explore PKD's role in Golgi organization, vesicle trafficking, and stress responses. By enabling precise detection of Ser738 phosphorylation, this tool aids in unraveling PKD's complex regulatory mechanisms and therapeutic potential in disease.
(Word count: 249)
×