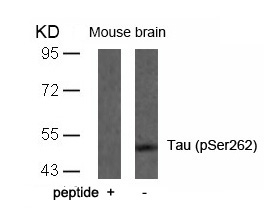
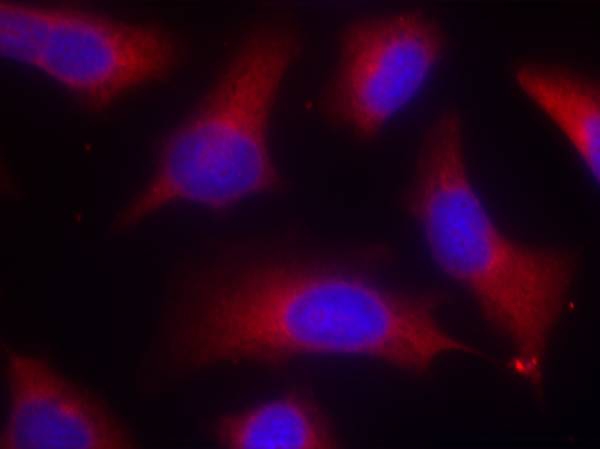
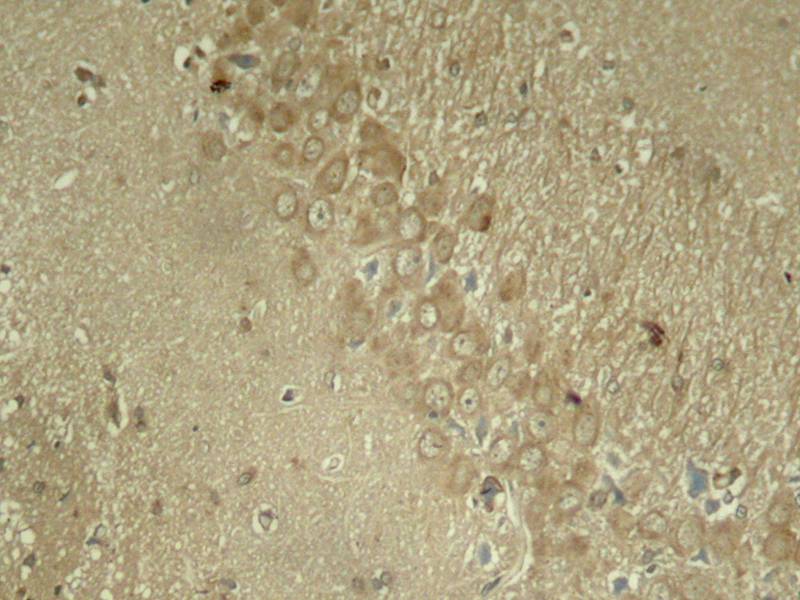
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MAPT; MTAPT; MTBT1; Neurofibrillary tangle protein; PHF-tau |
| Entrez GeneID | 4137; |
| WB Predicted band size | 48 62 78 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Peptide sequence around phosphorylation site of serine 262 (I-G-S(p)-T-E) derived from Human Tau. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于Tau (Phospho-Ser262)抗体的3篇参考文献示例,包含文献名称、作者及摘要内容概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Phosphorylation of Tau at Ser262 mediates binding to 14-3-3 protein and modulates microtubule stability*
**作者**:Yoshida H. et al.
**摘要**:本研究探讨了Tau蛋白在Ser262位点的磷酸化对14-3-3蛋白结合能力的影响。通过使用特异性抗体(Tau Phospho-Ser262)进行免疫印迹和免疫荧光分析,发现该位点的磷酸化导致Tau与微管的解离,并促进神经退行性变中异常蛋白聚集。
2. **文献名称**:*Altered Tau phosphorylation in Alzheimer’s disease: Role of GSK-3β activation at Ser262*
**作者**:Buee L. et al.
**摘要**:研究利用Tau Phospho-Ser262抗体分析阿尔茨海默病患者脑组织样本,发现糖原合成激酶-3β(GSK-3β)对Ser262的磷酸化显著增强。这种修饰与神经原纤维缠结的形成相关,并可能影响Tau的病理聚集。
3. **文献名称**:*Site-specific phosphorylation of Tau inhibits amyloid-β toxicity in Drosophila models*
**作者**:Steinhilb M.L. et al.
**摘要**:通过果蝇模型研究Tau磷酸化的功能,利用Tau Phospho-Ser262抗体证实Ser262的磷酸化可减轻Aβ诱导的神经毒性。实验表明该位点的修饰可能通过调节Tau的构象发挥神经保护作用。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例,实际引用时需核对具体发表信息及内容准确性。建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“Tau Phospho-Ser262 antibody”或“Tau phosphorylation Ser262”进一步筛选目标研究。
**Background of Tau (Phospho-Ser262) Antibody**
Tau is a microtubule-associated protein critical for stabilizing neuronal microtubules and maintaining axonal transport. In neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and related tauopathies, Tau undergoes abnormal hyperphosphorylation, leading to its dissociation from microtubules, aggregation into neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs), and neuronal dysfunction. Phosphorylation at specific residues, including Serine 262 (Ser262), is implicated in this pathological process.
The Tau (Phospho-Ser262) antibody specifically detects Tau phosphorylated at Ser262. a site located within the microtubule-binding domain. Phosphorylation at Ser262 is thought to reduce Tau’s affinity for microtubules, disrupting their stability. This modification is observed early in AD and correlates with disease progression, making it a key target for studying tau pathology.
Researchers use this antibody in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to assess phosphorylation-dependent Tau aggregation, map pathological changes in brain tissues, or evaluate therapeutic interventions targeting Tau phosphorylation. Its specificity helps distinguish disease-associated Tau isoforms from normal forms, aiding in mechanistic studies of tauopathies.
Commercial Tau (Phospho-Ser262) antibodies are often validated in models of AD, frontotemporal dementia, or transgenic mice expressing mutant Tau. However, cross-reactivity with non-target phospho-epitopes or splice variants requires careful validation. Understanding Ser262 phosphorylation dynamics provides insights into Tau’s pathological role and potential biomarkers or therapeutic strategies for neurodegenerative diseases.
×