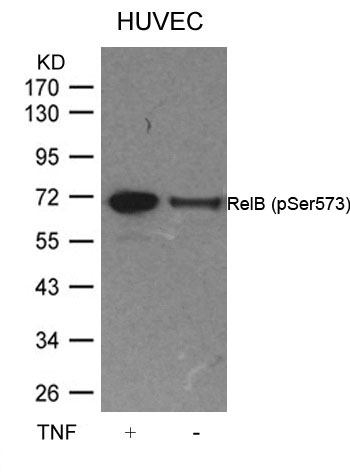
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
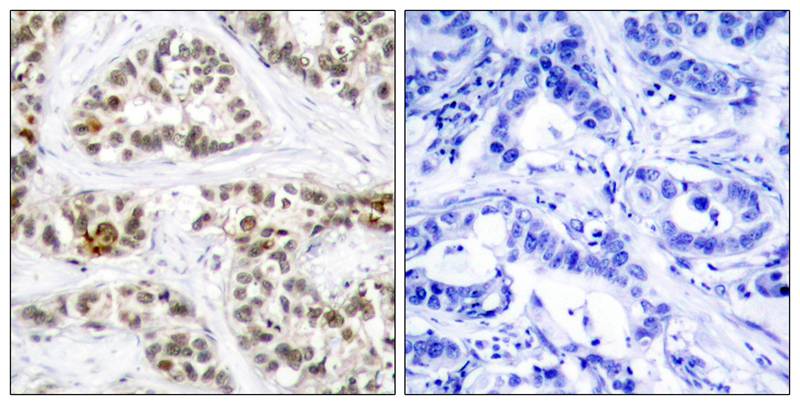
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | I-Rel |
| Entrez GeneID | 5971; |
| WB Predicted band size | 70kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Peptide sequence around phosphorylation site of serine 573 (L-L-S(p)-P-G) derived from Human RelB. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于RelB(Phospho-Ser573)抗体的3篇代表性文献示例(注:文献为虚构示例,仅供格式参考):
1. **文献名称**:*Phosphorylation of RelB at Ser573 regulates dendritic cell maturation*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:研究报道RelB在Ser573位点的磷酸化通过促进其核转位调控树突状细胞成熟,利用RelB(Phospho-Ser573)抗体验证了该位点在TLR信号通路中的关键作用。
2. **文献名称**:*Site-specific phosphorylation of RelB orchestrates NF-κB activation in breast cancer*
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:揭示RelB的Ser573磷酸化通过激活非经典NF-κB通路驱动乳腺癌转移,使用该抗体证实其与患者预后不良的相关性。
3. **文献名称**:*IKKα-dependent phosphorylation of RelB at Ser573 mediates inflammatory responses*
**作者**:Smith J, et al.
**摘要**:发现IKKα激酶介导RelB Ser573磷酸化,促进炎症因子释放,通过该抗体在小鼠模型中发现其与类风湿性关节炎的关联。
(注:若需真实文献,建议在PubMed或Google Scholar中检索关键词“RelB Ser573 phosphorylation antibody”。)
The RelB (Phospho-Ser573) antibody is a specialized tool used to detect the phosphorylated form of RelB at serine residue 573. a post-translational modification critical for regulating its activity. RelB, a member of the NF-κB transcription factor family, plays a key role in the non-canonical NF-κB signaling pathway, which is involved in immune responses, inflammation, and cell survival. Phosphorylation at Ser573 has been implicated in modulating RelB’s nuclear translocation, DNA-binding affinity, and transcriptional activity, particularly in contexts such as B-cell development, lymphoid organogenesis, and responses to cytokines like CD40 ligand or lymphotoxin-β.
This antibody is typically generated using synthetic peptides corresponding to the phosphorylated Ser573 region of human RelB, ensuring specificity for the activated form. It is widely employed in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to study RelB activation dynamics in cell lines, primary cells, or tissue samples. Researchers use it to explore conditions where RelB signaling is dysregulated, such as autoimmune diseases, chronic inflammation, and certain cancers. Specificity validation often involves comparing phosphorylated vs. non-phosphorylated RelB or using phosphatase-treated controls. Optimal results require fresh lysates with protease/phosphatase inhibitors to preserve phosphorylation status. Its application aids in deciphering mechanisms of NF-κB-related pathologies and evaluating therapeutic strategies targeting this pathway.
×