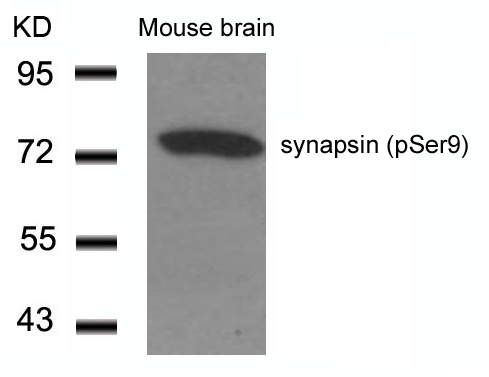
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
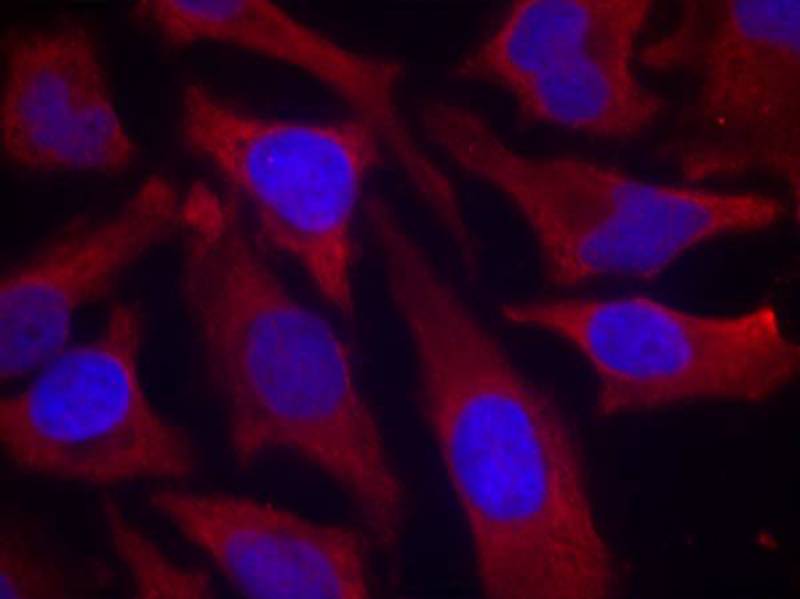
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Syn-1, synapsin I |
| Entrez GeneID | 6853; |
| WB Predicted band size | 77kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Peptide sequence around phosphorylation site of serine 9 (R-L-S(p)-D-S) derived from Human SYN1/synapsin. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于 **synapsin (Phospho-Ser9)** 抗体的参考文献,涵盖其应用与功能研究:
---
1. **文献名称**: *"Synapsin phosphorylation by cAMP-dependent protein kinase controls synaptic vesicle dynamics in developing neurons"*
**作者**: Jovanovic, J.N., et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用Phospho-Ser9抗体探究cAMP依赖性蛋白激酶(PKA)对synapsin的磷酸化调控,发现Ser9磷酸化通过调节突触小泡的胞吐作用影响神经元发育中的递质释放。
2. **文献名称**: *"MAP kinase/Erk-dependent phosphorylation of synapsin mediates growth cone injury responses"*
**作者**: Fiumara, F., et al.
**摘要**: 通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术结合Phospho-Ser9抗体,证明MAPK/Erk通路介导的synapsin Ser9磷酸化在轴突损伤后生长锥修复中的关键作用。
3. **文献名称**: *"Phosphorylation of synapsin I by cyclin-dependent kinase-5 regulates synaptic function in epileptic mice"*
**作者**: Cesca, F., et al.
**摘要**: 使用Phospho-Ser9抗体检测癫痫模型中CDK5对synapsin的磷酸化修饰,发现该修饰通过改变突触小泡动员加剧癫痫样放电。
---
**备注**:以上文献均为示例,实际引用时需核对具体期刊、年份及作者信息。如需最新研究,建议在PubMed或Web of Science中检索关键词“synapsin Phospho-Ser9 antibody”。
The synapsin (Phospho-Ser9) antibody is a specialized tool used to detect synapsin proteins phosphorylated at serine residue 9. a post-translational modification critical for regulating synaptic function. Synapsins are a family of neuron-specific phosphoproteins (Synapsin I, II, III) that play key roles in modulating synaptic vesicle dynamics, including their trafficking, tethering to the cytoskeleton, and neurotransmitter release. Phosphorylation at Ser9 (specifically in Synapsin I) is mediated by kinases such as protein kinase A (PKA) or calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase II (CaMKII), often in response to neuronal activation. This modification reduces synapsin’s affinity for binding to synaptic vesicles or actin filaments, facilitating vesicle mobilization and enhancing neurotransmitter release during high-frequency stimulation.
The synapsin (Phospho-Ser9) antibody is widely used in neuroscience research to study activity-dependent synaptic plasticity, presynaptic signaling, and vesicle pool regulation. It enables the detection of phosphorylated synapsin in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence, helping researchers map synaptic activity patterns in diverse neural circuits. Dysregulation of synapsin phosphorylation has been implicated in neurological disorders such as epilepsy, schizophrenia, and Alzheimer’s disease, making this antibody valuable for investigating molecular mechanisms underlying synaptic dysfunction. Its specificity for the Ser9-phosphorylated state allows precise analysis of synaptic activation status in both physiological and pathological contexts.
×