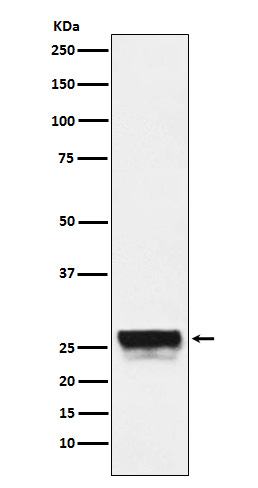
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CTRL; CTRL1;;CTRL |
| WB Predicted band size | Calculated MW: 28 kDa ; Observed MW: 24,28 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human CTRL |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.05% BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
1. **"Regulation of histone deacetylase 4 by binding of 14-3-3 proteins"**
- **作者**: Wang AH, et al.
- **摘要**: 该研究揭示了HDAC4的Ser246磷酸化如何促进与14-3-3蛋白的结合,导致HDAC4的核输出,从而抑制肌肉分化基因的表达。研究使用特异性抗体验证了该位点的磷酸化在细胞分化中的作用。
2. **"Signal-dependent nuclear export of a histone deacetylase regulates muscle differentiation"**
- **作者**: McKinsey TA, et al.
- **摘要**: 发现钙调神经磷酸酶信号通过诱导HDAC5的Ser259磷酸化,触发其核输出并激活肌肉特异性基因。抗体验证了磷酸化HDAC5在心肌细胞肥大中的动态调控。
3. **"Phosphorylation of HDAC9 by protein kinase D confers resistance to oxidative stress in cancer cells"**
- **作者**: Zhang Y, et al.
- **摘要**: 研究证明HDAC9的Ser220磷酸化由蛋白激酶D介导,增强癌细胞在氧化应激下的存活能力。通过特异性抗体证实该修饰在肿瘤模型中的促生存作用。
4. **"Class IIa histone deacetylases are hormone-activated regulators of nuclear receptor signaling"**
- **作者**: Fischle W, et al.
- **摘要**: 探讨IIa类HDACs(包括HDAC4/5/9)的磷酸化如何调控核受体信号通路。使用磷酸化特异性抗体揭示了不同激素刺激下HDACs亚细胞定位的变化机制。
**Background of HDAC4/HDAC5/HDAC9 (phospho-Ser246/259/220) Antibody**
Histone deacetylases (HDACs) 4. 5. and 9 belong to the class IIa HDAC family, which regulate gene expression by removing acetyl groups from histones, leading to chromatin condensation and transcriptional repression. These enzymes shuttle between the nucleus and cytoplasm, with their activity and localization tightly controlled by post-translational modifications, particularly phosphorylation. The phosphorylation of specific serine residues—Ser246 in HDAC4. Ser259 in HDAC5. and Ser220 in HDAC9—serves as a critical regulatory mechanism.
Phosphorylation at these sites is mediated by kinases such as calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase (CaMK) or salt-inducible kinase (SIK), often in response to extracellular signals. This modification promotes binding to 14-3-3 chaperone proteins, sequestering HDAC4/5/9 in the cytoplasm and preventing their nuclear translocation. Consequently, their interaction with transcription factors (e.g., MEF2) is disrupted, derepressing target genes involved in processes like muscle differentiation, neuronal survival, and immune regulation. Dysregulation of these phosphorylation events is linked to diseases, including cancer, cardiac hypertrophy, and neurodegenerative disorders.
Antibodies targeting HDAC4/HDAC5/HDAC9 phosphorylated at Ser246/259/220 are essential tools for studying the activation status of these enzymes, their subcellular localization, and their role in signaling pathways. They enable detection of phosphorylation-dependent regulatory mechanisms in cell and tissue samples, aiding research into therapeutic strategies targeting class IIa HDACs. Specificity for phosphorylated forms ensures accurate assessment of pathway activity in physiological or disease contexts.
×