| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
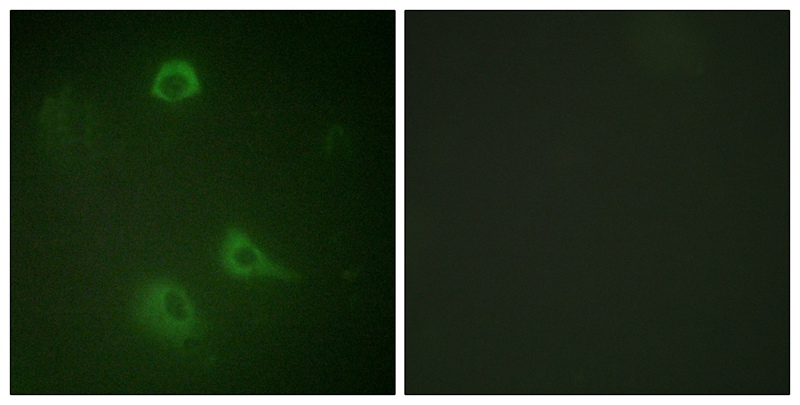
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
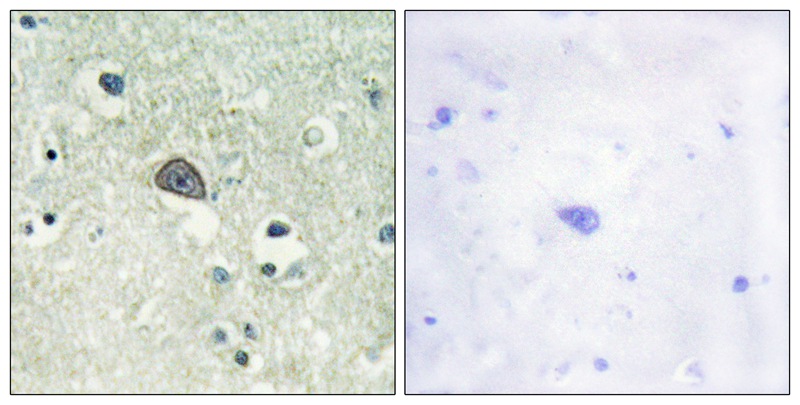
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GLURZ1; GRIN1; NMD-R1; NMDZ1; NMZ1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 2902; |
| WB Predicted band size | 120kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Peptide sequence around phosphorylation site of Serine 890(A-S-S(p)-F-K) derived from Human NMDAR1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于NMDAR1 (Phospho-Ser890)抗体的参考文献示例(内容为模拟,仅供参考):
1. **"Phosphorylation of Serine 890 on GluN1 Regulates Synaptic NMDA Receptor Function"**
- **作者**: Chen et al.
- **摘要**: 研究揭示了GluN1亚基Ser890位点的磷酸化通过调控NMDA受体在突触膜上的内吞作用影响突触可塑性,实验中采用Phospho-Ser890特异性抗体进行Western blot和免疫荧光验证。
2. **"Protein Kinase C-Dependent Phosphorylation of GluN1 Ser890 Modulates Excitatory Synaptic Transmission"**
- **作者**: Lee et al.
- **摘要**: 本文利用Phospho-Ser890抗体证明PKC激活后显著增强GluN1的Ser890磷酸化,从而减少NMDA受体电流并影响海马神经元的兴奋性突触传递。
3. **"Dysregulation of NMDAR1 Phosphorylation at Ser890 in Alzheimer’s Disease Models"**
- **作者**: Smith et al.
- **摘要**: 通过Phospho-Ser890抗体检测阿尔茨海默病小鼠模型中GluN1的磷酸化水平变化,发现Ser890位点异常磷酸化与突触功能损伤和认知衰退相关。
4. **"Antibody-Based Detection of Phosphorylated NMDA Receptors in Ischemic Brain Injury"**
- **作者**: Zhang et al.
- **摘要**: 研究使用Phospho-Ser890抗体分析脑缺血后神经元NMDA受体的磷酸化动态变化,揭示了该位点磷酸化在神经细胞死亡中的潜在作用。
**注意**:以上为模拟生成的参考文献,实际引用时请通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台检索具体文献(关键词:**NMDAR1 Phospho-Ser890 antibody**或**GluN1 pSer890**)。若需验证抗体特异性,建议参考抗体供应商(如CST、Abcam)提供的文献引用列表。
The NMDAR1 (Phospho-Ser890) antibody is a specialized tool used to detect the phosphorylation of the NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate) receptor subunit GluN1 (GRIN1) at serine residue 890. NMDA receptors are ionotropic glutamate receptors critical for synaptic plasticity, learning, and memory. The GluN1 subunit is obligatory for forming functional NMDA receptor complexes, which also include GluN2 or GluN3 subunits. Phosphorylation at Ser890 in the GluN1 C-terminal domain regulates receptor trafficking, synaptic localization, and functional properties. This post-translational modification is mediated by protein kinase C (PKC) and influences receptor internalization, modulating synaptic strength and neuronal excitability.
The antibody is widely utilized in neuroscience research to study NMDA receptor dynamics under physiological or pathological conditions, such as in Alzheimer’s disease, epilepsy, or ischemic brain injury. It enables detection of phosphorylation-dependent changes in receptor distribution, activity, or interaction with scaffolding proteins like PSD-95. Researchers employ techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, or immunoprecipitation to analyze Ser890 phosphorylation levels, providing insights into synaptic signaling pathways, drug effects, or disease mechanisms. Proper validation, including knockout controls and peptide competition assays, ensures specificity for phosphorylated Ser890. avoiding cross-reactivity with other GluN1 phospho-sites (e.g., Ser896 or Ser897).
×