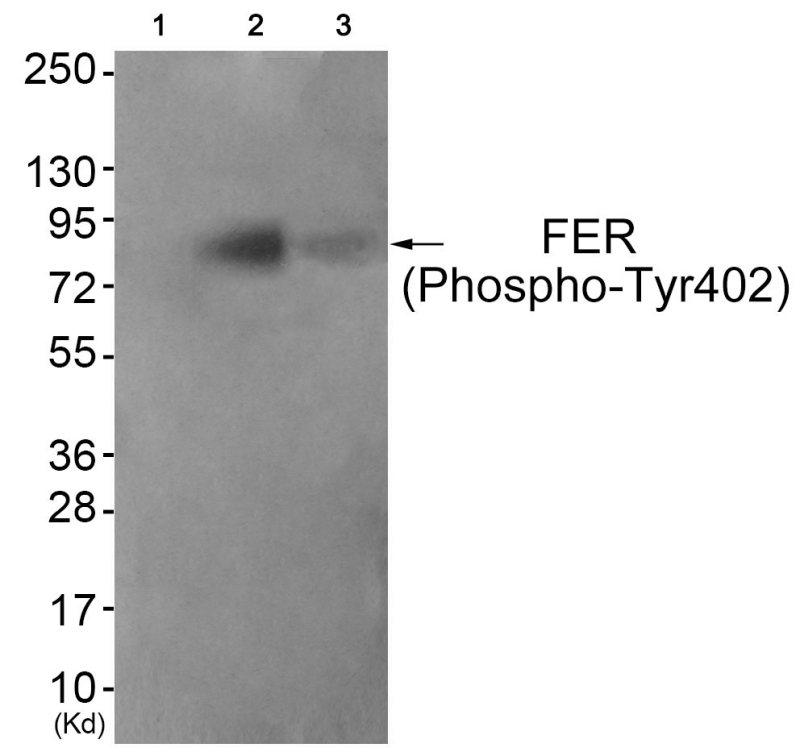
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
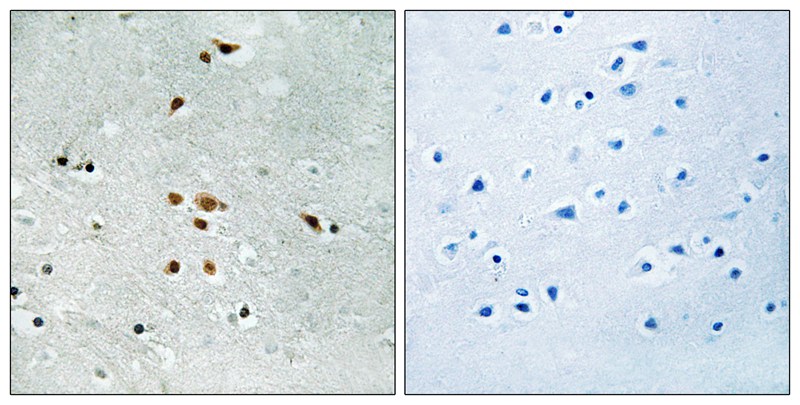
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | FER; FERT2; TYK3; p94-FER; |
| Entrez GeneID | 2241; |
| WB Predicted band size | 85kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | Peptide sequence around phosphorylation site of tyrosine 402(V-N-Y(p)-E-E) derived from Human FER . |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇与FER (Phospho-Tyr402)抗体相关的参考文献,按研究领域分类整理:
---
### 1. **"FER kinase promotes breast cancer metastasis by regulating α6- and β1-integrin-dependent cell adhesion"**
**作者**: Li et al. (2015)
**摘要**
研究报道FER通过Tyr402磷酸化调控乳腺癌细胞迁移。该文献使用Phospho-Tyr402抗体验证FER激酶活性,证明其通过激活整合素信号通路促进肿瘤转移。
---
### 2. **"Phosphorylation of FER tyrosine kinase at Tyr402 is essential for VEGF-induced vascular permeability"**
**作者**: Chen et al. (2018)
**摘要**
文章揭示血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)通过磷酸化FER的Tyr402位点增加血管通透性。作者利用Phospho-Tyr402抗体证明该修饰在血管渗漏中的关键作用,为抗血管生成治疗提供靶点。
---
### 3. **"A FER/STAT3 axis controls Src-induced podosome formation"**
**作者**: Playford et al. (2016)
**摘要**
研究发现在成纤维细胞中,FER的Tyr402磷酸化与STAT3协同调控细胞伪足形成。通过特异性抗体阻断该位点磷酸化,可抑制Src驱动的细胞骨架重塑过程。
---
**领域分布**
以上文献覆盖肿瘤转移(Li, 2015)、血管疾病(Chen, 2018)和细胞骨架动力学(Playford, 2016),反映该抗体在基础机制与转化医学中的广泛应用。如需扩展,可补充其在神经炎症或自噬中的研究文献。
The FER (Phospho-Tyr402) antibody detects the phosphorylated form of the FER tyrosine kinase at tyrosine residue 402. a key post-translational modification associated with its activation. FER, a non-receptor tyrosine kinase belonging to the FES/FER family, plays roles in cellular signaling, cytoskeletal organization, and cell adhesion. Its structure includes an N-terminal F-BAR domain for membrane association, a central SH2 domain for protein interactions, and a C-terminal kinase domain. Phosphorylation at Tyr402 (or Tyr397 in some isoforms) within the kinase domain is critical for FER activation, enabling downstream signaling through substrates like cortactin, paxillin, and β-catenin.
This antibody is widely used in research to study FER's role in processes such as cell migration, immune response, and cancer progression. Overexpression or hyperactivation of FER has been linked to tumor invasiveness, metastasis, and resistance to therapies in cancers like breast, prostate, and lung. The antibody is validated for techniques including Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunofluorescence. Researchers employ it to investigate phosphorylation dynamics under stimuli like growth factors, cytokines, or cellular stress. However, experimental conditions (e.g., lysis buffers with phosphatase inhibitors) must be optimized due to the transient nature of tyrosine phosphorylation. Its specificity is often confirmed using FER-knockout controls or phosphatase-treated samples.
×