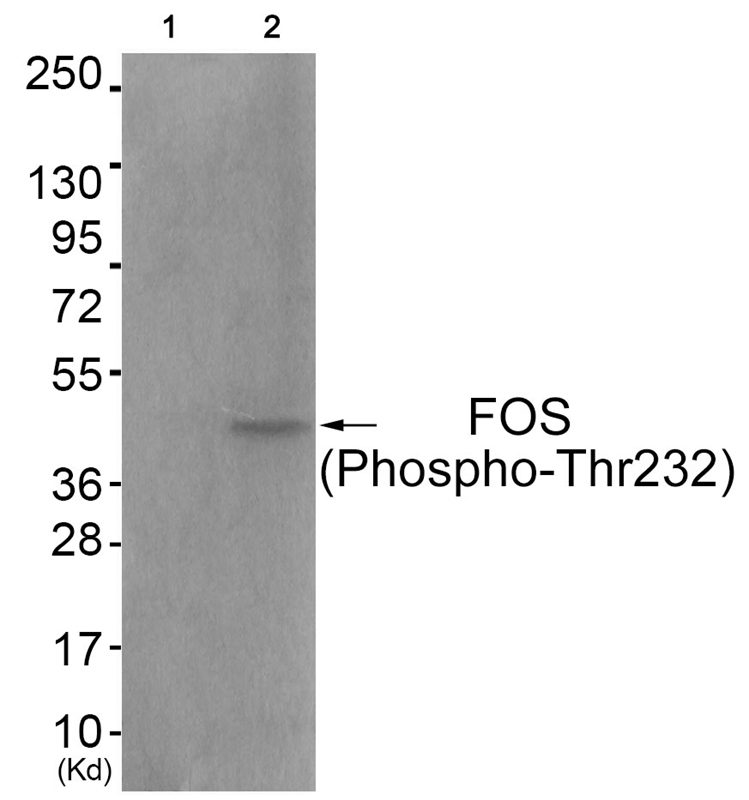
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
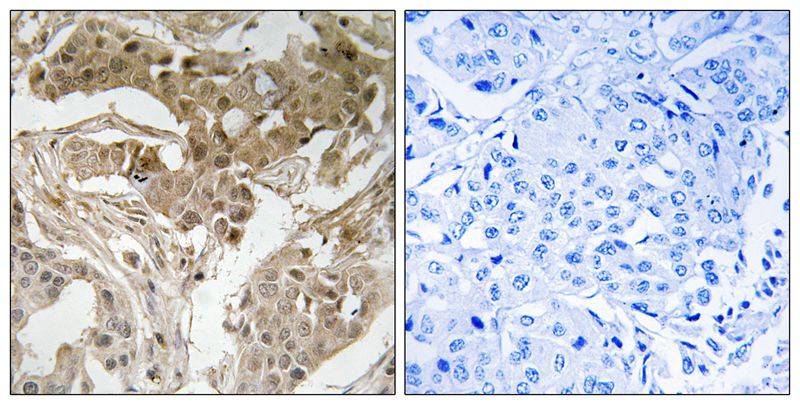
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | FOS; G0S7; Cellular oncogene fos; |
| Entrez GeneID | 2353; |
| WB Predicted band size | 48kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Peptide sequence around phosphorylation site of threonine 232(V-A-T(p)-P-E) derived from Human FOS . |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于FOS (Phospho-Thr232)抗体的参考文献摘要概览:
---
1. **"Phosphorylation of c-Fos at Threonine 232 Regulates Its Nuclear Localization"**
*作者:Chen et al.*
摘要:研究通过磷酸化特异性抗体发现,c-Fos Thr232位点的磷酸化通过影响其与核转运蛋白的相互作用,调控其在DNA损伤后的核内定位,并增强AP-1转录活性。
---
2. **"MAPK-mediated phosphorylation of c-Fos Thr232 modulates osteoclast differentiation"**
*作者:Miyazaki et al.*
摘要:利用Phospho-Thr232抗体证实,MAPK通路介导的该位点磷酸化是破骨细胞分化的关键步骤,抑制该位点磷酸化可减少骨吸收相关基因表达。
---
3. **"Site-specific phosphorylation of c-Fos by AMPK links metabolic stress to cell cycle progression"**
*作者:Harper et al.*
摘要:通过Western blot和免疫荧光(使用Phospho-Thr232抗体),发现能量应激下AMPK直接磷酸化c-Fos Thr232.导致细胞周期停滞并促进自噬。
---
提示:建议通过PubMed或抗体供应商(如CST的#5345)获取具体文献全文。
The FOS (Phospho-Thr232) antibody is a specialized tool used to detect the phosphorylated form of the FOS protein at threonine residue 232. FOS, a proto-oncogene product, is a key component of the AP-1 transcription factor complex, which regulates gene expression in response to cellular stimuli like growth factors, stress, or cytokines. Phosphorylation plays a critical role in modulating FOS stability, activity, and interactions with partner proteins such as JUN family members. The Thr232 phosphorylation site is implicated in post-translational regulation, potentially influencing FOS’s nuclear localization, protein-protein interactions, or degradation.
This antibody is widely employed in research to study FOS activation dynamics in pathways related to cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and oncogenesis. It enables the identification of phosphorylated FOS in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, or immunohistochemistry, helping researchers assess FOS’s functional state under specific conditions (e.g., mitogen stimulation, oxidative stress, or disease models). Its specificity for the phosphorylated epitope makes it valuable for investigating temporal signaling events or dysregulated pathways in cancers, neurological disorders, or inflammatory diseases. Proper validation using phosphorylation-specific controls (e.g., phosphatase treatment) is essential to ensure accurate interpretation of results.
×