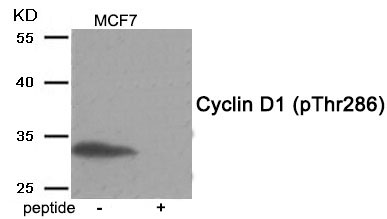
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | BCL-1 ; oncogene; CYL-1; PRAD1; PRAD1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 595; |
| WB Predicted band size | 33kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Peptide sequence around phosphorylation site of threonine 286 (A-C-T(p)-P-T) derived from Human Cyclin D1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于Cyclin D1 (Phospho-Thr286)抗体的3篇参考文献摘要:
1. **文献名称**:*Phosphorylation-dependent degradation of p27Kip1 by cyclin D1-CDK4*
**作者**:Diehl, J.A. 等
**摘要**:该研究揭示了Cyclin D1在Thr286位点的磷酸化对其核质转运和蛋白酶体降解的关键作用,并验证了Phospho-Thr286特异性抗体在Western blot中的应用,证明其与细胞周期调控相关。
2. **文献名称**:*Cyclin D1 phosphorylation at Thr-286 regulates its subcellular localization and oncogenic activity*
**作者**:Lin, D.I. 等
**摘要**:作者利用Phospho-Thr286抗体通过免疫荧光和Western blot分析,发现该位点的磷酸化异常与乳腺癌进展相关,并影响Cyclin D1的致癌功能。
3. **文献名称**:*Cyclin D1 degradation is sufficient to induce G1 cell cycle arrest*
**作者**:Tchakarska, G. 等
**摘要**:研究通过Phospho-Thr286抗体检测淋巴瘤细胞中Cyclin D1的磷酸化状态,证明Thr286磷酸化介导的降解是G1期阻滞的关键机制。
4. **文献名称**:*Phosphorylation of cyclin D1 at Thr286 during mitosis leads to its cytoplasmic localization*
**作者**:Bienvenu, F. 等
**摘要**:该文献利用特异性抗体验证Thr286磷酸化在细胞有丝分裂中的作用,揭示其通过核输出信号调控Cyclin D1亚细胞定位的功能。
这些研究均通过Phospho-Thr286抗体探索了该位点在细胞周期、癌症及蛋白降解中的分子机制。
Cyclin D1 (Phospho-Thr286) antibodies are essential tools for studying cell cycle regulation and oncogenesis. Cyclin D1. a key regulator of the G1/S phase transition, forms complexes with cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK4/6) to phosphorylate retinoblastoma (Rb) protein, promoting cell cycle progression. Phosphorylation at Thr286 is a critical post-translational modification that triggers Cyclin D1 nuclear export and subsequent proteasomal degradation, ensuring timely cell cycle exit or DNA damage response. Dysregulation of this process—due to Cyclin D1 overexpression or impaired phosphorylation—is linked to uncontrolled proliferation and tumorigenesis, notably in cancers like breast cancer, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma.
Antibodies specific for Cyclin D1 phosphorylated at Thr286 enable researchers to detect and quantify this activated form in various experimental settings, including Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF). They are particularly valuable for investigating mechanisms of cell cycle arrest, DNA damage responses, and the effects of therapeutic agents targeting CDK4/6 or upstream signaling pathways (e.g., Ras/MAPK, PI3K/Akt). These antibodies also help elucidate how oncogenic mutations or epigenetic alterations disrupt Cyclin D1 degradation, contributing to tumor progression. Validation in phospho-specific assays and knockout controls is crucial to ensure specificity, given the structural similarity among cyclin family members.
×