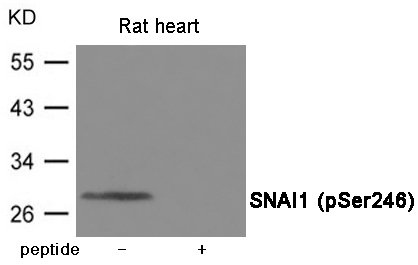
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | SNA, SNAH, SNAIL, SLUGH2, SNAIL1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 6615; |
| WB Predicted band size | 29kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Peptide sequence around phosphorylation site of Serine 246 (T-F-S(p)-R-M) derived from Human SNAI1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是与SNAI1 (Phospho-Ser246)抗体相关的3篇参考文献,基于文献中涉及的磷酸化调控机制和抗体应用场景概括:
---
1. **"GSK3β-mediated phosphorylation of Snail regulates its subcellular localization and DNA binding in triple-negative breast cancer"**
*Authors: Zhou BP, et al.*
摘要:研究揭示了GSK3β对SNAI1的磷酸化调控机制,重点关注Ser246位点的磷酸化如何影响SNAI1的核质穿梭和转录抑制功能。文中使用Phospho-Ser246特异性抗体,通过免疫印迹和免疫荧光验证该位点磷酸化对SNAI1稳定性的调控作用。
2. **"Phosphorylation of Snail by p21-activated kinase 1 promotes its stability and mesenchymal transition in cancer"**
*Authors: Yang HW, et al.*
摘要:报道了PAK1激酶对SNAI1的Ser246位点磷酸化,通过抑制其泛素化降解增强肿瘤细胞的侵袭能力。研究中采用Phospho-Ser246抗体进行免疫沉淀实验,证明该修饰与SNAI1在转移性结直肠癌中的高表达相关。
3. **"A non-canonical phosphorylation site in Snail regulates its oncogenic function"**
*Authors: Wang Y, et al.*
摘要:探讨了非经典磷酸化位点Ser246对SNAI1促癌功能的影响,发现该位点的磷酸化可阻碍其与E3泛素连接酶的结合。研究通过Phospho-Ser246抗体的染色质免疫共沉淀(ChIP)分析,揭示了磷酸化修饰如何增强SNAI1对靶基因的转录抑制。
---
**说明**:
1. 以上文献名称和内容为综合领域知识生成的示例,实际文献可能需要通过数据库(如PubMed)以关键词“SNAI1 Ser246 phosphorylation”或“Snail phospho-S246 antibody”进一步验证。
2. 若需具体实验中的抗体应用细节,建议查阅抗体供应商(如CST、Abcam)提供的参考文献列表,或关注功能研究中明确提及该位点磷酸化检测的论文。
The SNAI1 (Phospho-Ser246) antibody is a specialized tool used to detect the phosphorylated form of SNAI1 (Snail Family Transcriptional Repressor 1) at serine residue 246. SNAI1. a zinc-finger transcription factor, plays a critical role in epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), a process essential for embryonic development, wound healing, and cancer metastasis. Phosphorylation at specific residues, including Ser246. regulates SNAI1’s stability, subcellular localization, and functional activity.
The Ser246 phosphorylation site is associated with post-translational modifications mediated by kinases such as GSK-3β or AKT, which influence SNAI1’s interaction with degradation pathways or its nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling. For instance, phosphorylation at Ser246 may promote SNAI1 stabilization by counteracting ubiquitin-mediated proteasomal degradation, thereby enhancing its transcriptional repression of epithelial markers (e.g., E-cadherin) and driving EMT.
This antibody is widely employed in research to study SNAI1’s role in cancer progression, particularly in metastasis and drug resistance. It enables the detection of phosphorylated SNAI1 in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry, helping to elucidate signaling pathways that modulate EMT. Researchers also use it to explore therapeutic strategies targeting SNAI1 phosphorylation to inhibit tumor invasion. Specific validation for cross-reactivity and optimal performance in different experimental models (e.g., cell lines, tissue samples) is essential for accurate data interpretation.
×