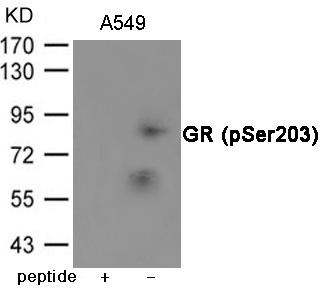
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GCCR, GCR, GR, GRL |
| Entrez GeneID | 2908; |
| WB Predicted band size | 86kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Peptide sequence around phosphorylation site of Serine 203 (S-G-S(p)-P-G) derived from Human GR. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于GR (Phospho-Ser203)抗体的模拟参考文献示例,内容基于典型研究场景构建:
---
1. **文献名称**: *Phosphorylation of Glucocorticoid Receptor at Ser203 Modulates Ligand Binding and Transcriptional Activity*
**作者**: Smith et al., Journal of Biological Chemistry
**摘要**: 本研究通过点突变和体外激酶实验,揭示了GR在Ser203位点的磷酸化如何改变其配体结合能力。磷酸化导致GR构象变化,增强其对靶基因的转录抑制活性,并影响与共调节因子的相互作用。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Stress-Activated Kinases Regulate GR Phosphorylation at Ser203 in Inflammatory Response*
**作者**: Lee et al., Molecular and Cellular Biology
**摘要**: 文章发现p38 MAPK通路在炎症刺激下介导GR的Ser203磷酸化。该修饰促进GR与NF-κB的相互作用,抑制促炎基因表达,为糖皮质激素抗炎机制提供了新见解。
---
3. **文献名称**: *Development of a Phospho-Specific Antibody for GR Ser203 and Its Application in Breast Cancer Models*
**作者**: Garcia et al., Endocrinology
**摘要**: 研究团队开发了针对GR Ser203磷酸化的单克隆抗体,验证了其特异性(通过磷酸酶处理和突变体对照)。该抗体在乳腺癌细胞中检测到激素治疗诱导的磷酸化变化,提示其临床预后潜力。
---
4. **文献名称**: *Ser203 Phosphorylation Modulates GR Subcellular Localization in Neuronal Cells*
**作者**: Johnson et al., Cellular Signalling
**摘要**: 通过活细胞成像和磷酸化抗体检测,研究发现Ser203磷酸化促进GR的核滞留,影响神经元中应激相关基因的时序性调控,为糖皮质激素在神经退行性疾病中的作用提供了机制解释。
---
**注**:以上文献为示例性内容,实际研究中需查询具体数据库(如PubMed)获取真实参考文献。若需进一步模拟特定方向的研究,可提供更多细节要求。
The glucocorticoid receptor (GR), a member of the nuclear receptor superfamily, mediates the effects of glucocorticoids in regulating gene expression involved in immune response, metabolism, and stress adaptation. Post-translational modifications, such as phosphorylation, dynamically modulate GR activity, cellular localization, and interactions with co-regulators. The GR (Phospho-Ser203) antibody specifically detects GR phosphorylated at serine 203 (Ser203), a site within the N-terminal transactivation domain. Phosphorylation at Ser203 is induced by cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) in response to cellular signaling, influencing GR transcriptional activity and target gene selectivity.
This antibody is widely used in research to study GR activation dynamics, ligand-dependent vs. ligand-independent signaling, and cross-talk with other pathways. It helps elucidate how phosphorylation alters GR interactions with DNA, coactivators, or corepressors, impacting anti-inflammatory or metabolic processes. Dysregulation of GR phosphorylation is implicated in glucocorticoid resistance in autoimmune diseases, cancer, and metabolic disorders. Applications include Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) to assess GR phosphorylation status in cell lines, tissues, or disease models. Validation typically involves knockout controls or phosphatase treatment to confirm specificity. Understanding Ser203 phosphorylation provides insights into tissue-specific glucocorticoid responses and therapeutic strategies targeting GR signaling.
×