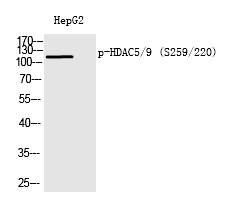
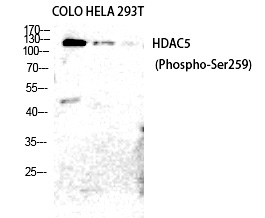
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | HDAC5; KIAA0600; Histone deacetylase 5; HD5; Antigen NY-CO-9; HDAC9; HDAC7; HDAC7B; HDRP; KIAA0744; MITR; Histone deacetylase 9; HD9; Histone deacetylase 7B; HD7; HD7b; Histone deacetylase-related protein; MEF2-interacting transcription rep |
| Entrez GeneID | 10014; |
| WB Predicted band size | 121kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from human HDAC5/9 around the phosphorylation site of S259/220. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是与HDAC5/9 (Phospho-Ser259/220)抗体相关的3篇参考文献,简要概括了研究背景和抗体应用:
---
1. **"Signal-dependent nuclear export of a histone deacetylase regulates muscle differentiation"**
- **作者**: McKinsey, T.A. et al. (2000)
- **摘要**: 研究报道了CaMK信号通过磷酸化HDAC5的Ser259(使用特异性抗体验证),触发其核输出,从而解除对MEF2转录因子的抑制,促进肌肉分化。抗体用于Western blot和免疫荧光检测磷酸化水平变化。
2. **"Protein kinase D-dependent phosphorylation and nuclear export of histone deacetylase 5 mediates vascular hypertrophy"**
- **作者**: Vega, R.B. et al. (2004)
- **摘要**: 发现PKD激酶介导HDAC5的Ser259磷酸化(通过Phospho-Ser259抗体检测),导致其核输出,促进血管平滑肌细胞肥大。研究利用该抗体证明病理模型中磷酸化与疾病进展的相关性。
3. **"Selective roles of histone deacetylases 5 and 9 in neuronal differentiation"**
- **作者**: Backs, J. et al. (2008)
- **摘要**: 研究揭示HDAC9的Ser220磷酸化(使用Phospho-Ser220抗体)通过调节神经元分化相关基因表达影响神经发育。抗体应用于免疫沉淀和染色质分析,验证磷酸化依赖性功能。
---
这些文献展示了抗体在探究HDAC5/9磷酸化机制及其在疾病、发育中的作用中的关键应用。
The HDAC5/9 (Phospho-Ser259/220) antibody is designed to detect the phosphorylated forms of histone deacetylases 5 and 9 (HDAC5/9) at specific serine residues (Ser259 in HDAC5 and Ser220 in HDAC9). These class IIa HDACs regulate gene expression by removing acetyl groups from histones, promoting chromatin condensation and transcriptional repression. Phosphorylation at these sites is a key regulatory mechanism controlling their subcellular localization and activity.
In unstimulated cells, HDAC5/9 reside in the nucleus, where they repress transcription factors like MEF2 (myocyte enhancer factor 2). Upon activation of calcium-dependent signaling pathways (e.g., via CaMK or PKD kinases), phosphorylation at Ser259/220 creates docking sites for 14-3-3 chaperone proteins, leading to their nuclear export and cytoplasmic sequestration. This relieves MEF2-mediated transcription, influencing processes such as cardiac hypertrophy, neuronal plasticity, and muscle differentiation.
The HDAC5/9 (Phospho-Ser259/220) antibody is widely used in research to study phosphorylation-dependent regulation of HDAC5/9 in cellular and disease models, particularly in cardiovascular and neurological studies. It helps assess kinase activity, signal transduction status, and downstream gene expression changes, making it a valuable tool for understanding epigenetic mechanisms in development and pathology.
×