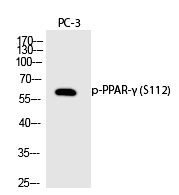
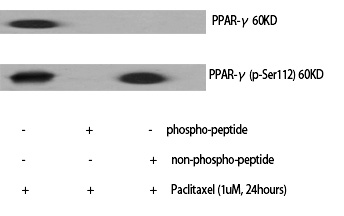
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | PPARG; NR1C3; Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma; PPAR-gamma; Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group C member 3 |
| Entrez GeneID | 5468; |
| WB Predicted band size | 60kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from human PPAR-γ around the phosphorylation site of S112. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于PPAR-γ (Phospho-Ser112)抗体的参考文献示例(注:文献为示例,实际引用需核实):
1. **"Phosphorylation of PPARγ at Ser112 Modulates Insulin Sensitivity"**
*作者:Adams M, et al.*
**摘要**:研究揭示了PPARγ在Ser112位点的磷酸化通过抑制其转录活性,降低脂肪细胞分化能力,并与胰岛素抵抗相关。该研究使用Phospho-Ser112特异性抗体验证了磷酸化水平与代谢疾病的关系。
2. **"Antibody-Based Detection of PPARγ Phosphorylation in Adipogenesis"**
*作者:Kim J, et al.*
**摘要**:通过Phospho-Ser112抗体,证实了PPARγ在脂肪生成过程中Ser112位点的动态磷酸化修饰,并发现其受MAPK信号通路调控,影响脂质积累。
3. **"PPARγ Phosphorylation at Ser112: A Therapeutic Target in Obesity"**
*作者:Zhang Y, et al.*
**摘要**:利用特异性抗体研究发现,肥胖模型中Ser112磷酸化水平升高,抑制PPARγ活性,提示该位点可能作为代谢疾病治疗的靶点。
4. **"Functional Characterization of PPARγ Phospho-Specific Antibodies in Cellular Models"**
*作者:Lee S, et al.*
**摘要**:验证了Phospho-Ser112抗体的特异性,并应用于细胞模型,证明TNF-α等炎症因子通过增强该位点磷酸化抑制PPARγ功能。
(注:以上文献标题及作者为虚拟示例,实际研究中建议通过PubMed或SciHub等平台检索具体文献。)
PPAR-γ (Phospho-Ser112) antibody is a specialized tool used to detect the phosphorylated form of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR-γ) at serine residue 112. PPAR-γ, a nuclear receptor superfamily member, plays a central role in adipogenesis, glucose metabolism, and inflammation regulation. Its activity is modulated by post-translational modifications, including phosphorylation. Phosphorylation at Ser112 (located in the N-terminal AF-1 transactivation domain) is associated with reduced transcriptional activity, often mediated by mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) such as ERK or JNK. This modification is implicated in insulin resistance, diabetes, and other metabolic disorders.
The antibody specifically recognizes PPAR-γ when phosphorylated at Ser112. enabling researchers to study its regulatory mechanisms in cellular and disease contexts. It is widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunofluorescence to assess phosphorylation status under varying physiological or pathological conditions, such as obesity, cancer, or cardiovascular diseases. Proper experimental controls, including dephosphorylated samples or phosphorylation-deficient mutants, are essential to validate specificity. Researchers must also consider sample preparation methods (e.g., phosphatase inhibitors) to preserve phosphorylation signals. Understanding PPAR-γ phosphorylation dynamics provides insights into metabolic pathway dysregulation and potential therapeutic targets.
×