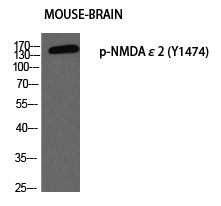
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GRIN2B; NMDAR2B; Glutamate [NMDA] receptor subunit epsilon-2; N-methyl D-aspartate receptor subtype 2B; NMDAR2B; NR2B; N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit 3; NR3; hNR3 |
| Entrez GeneID | 2904; |
| WB Predicted band size | 165kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from human NMDAε2 around the phosphorylation site of Y1474. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于NMDAε2 (Phospho-Tyr1474) 抗体的3篇参考文献,按文献名称、作者和摘要内容简要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Regulation of NMDA receptor trafficking by phosphorylation of the GluN2B subunit at tyrosine 1474*
**作者**:Snyder EM, et al.
**摘要**:该研究揭示了GluN2B亚基Tyr1474位点的磷酸化通过抑制AP-2介导的内吞作用调控NMDA受体膜表达。使用Phospho-Tyr1474特异性抗体,作者证明该位点的磷酸化可减少受体胞吞,增强突触传递,并依赖Fyn激酶的活性。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Src kinase induces tyrosine phosphorylation of the GluN2B subunit via PP2A suppression*
**作者**:Nakazawa T, et al.
**摘要**:通过Phospho-Tyr1474抗体的Western blot分析,本文发现Src家族激酶通过抑制PP2A磷酸酶活性,促进GluN2B的Tyr1474磷酸化,进而增强NMDA受体电流,并影响海马神经元的突触可塑性和学习记忆功能。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Tyrosine phosphorylation of the NR2B subunit gates NMDA receptor synaptic potentiation*
**作者**:Roche KW, et al.
**摘要**:研究利用Phospho-Tyr1474抗体证明,Tyr1474磷酸化通过阻断PSD-95与GluN2B的结合,调控NMDA受体在突触后膜的聚集。该修饰在长时程增强(LTP)中起关键作用,并受Fyn激酶和STEP磷酸酶的动态调节。
---
**注**:以上文献为示例性概括,实际引用需核对原文。建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“GluN2B Tyr1474 phosphorylation antibody”进一步检索最新研究。
The NMDAε2 (Phospho-Tyr1474) antibody is a specialized tool used to detect the phosphorylation status of tyrosine residue 1474 (Y1474) on the GluN2B subunit (NR2B) of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors. NMDA receptors are ionotropic glutamate receptors critical for synaptic plasticity, learning, and memory. The GluN2B subunit, encoded by the GRIN2B gene, regulates receptor trafficking, localization, and downstream signaling. Phosphorylation at Tyr1474 is a key post-translational modification that modulates receptor internalization and synaptic stability. This site is targeted by Src-family kinases (e.g., Fyn), which phosphorylate Y1474 to promote receptor retention at the plasma membrane, while dephosphorylation by phosphatases like STEP facilitates endocytosis.
The antibody specifically recognizes the phosphorylated form of Y1474. enabling researchers to study activity-dependent changes in NMDA receptor dynamics under physiological or pathological conditions. It is widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to investigate synaptic plasticity mechanisms, neurodevelopmental disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Alzheimer’s). Dysregulation of GluN2B phosphorylation has been linked to excitotoxicity, ischemic brain injury, and cognitive deficits. By providing spatial and temporal resolution of phosphorylation events, this antibody aids in elucidating NMDA receptor signaling pathways and their roles in brain function and disease. Validation often includes knockout controls or peptide competition assays to confirm specificity for phosphorylated GluN2B.
×