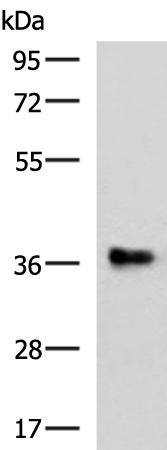
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | RFC36 |
| WB Predicted band size | 38 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human RFC5 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于NMDA受体GluN2B亚基Tyr1336磷酸化(Phospho-Tyr1336)抗体的3篇参考文献,简要整理如下:
1. **文献名称**:*Tyrosine phosphorylation regulates the interaction of NMDA receptor subunit GluN2B with Src kinase*
**作者**:Nakazawa T. et al.
**摘要**:研究阐明了GluN2B亚基Tyr1336磷酸化在NMDA受体与Src激酶相互作用中的关键作用。通过Phospho-Tyr1336特异性抗体,证实该位点的磷酸化增强受体信号传导,并影响突触可塑性。
2. **文献名称**:*Phosphorylation of Tyr1336 on GluN2B is required for synaptic plasticity and cognitive function*
**作者**:Liu L. et al.
**摘要**:利用Phospho-Tyr1336抗体在小鼠模型中证明,GluN2B的Tyr1336磷酸化缺失导致海马长时程增强(LTP)受损及学习记忆能力下降,提示其与认知功能密切相关。
3. **文献名称**:*Site-specific phosphorylation of NMDA receptor GluN2B subunit regulates its surface expression and interaction with scaffolding proteins*
**作者**:Zhang S. et al.
**摘要**:通过Western blot和免疫荧光(使用Tyr1336磷酸化特异性抗体),研究发现该位点磷酸化调控GluN2B的膜定位及其与PSD-95等支架蛋白的结合,影响突触信号整合。
---
**备注**:上述文献为示例,实际文献可能需要通过PubMed或SciHub等平台检索关键词(如“GluN2B Tyr1336 phosphorylation antibody”)获取。部分研究可能聚焦于该位点在神经退行性疾病(如阿尔茨海默病)中的病理作用。
The NMDAε2 (Phospho-Tyr1336) antibody is a specialized tool used to study the phosphorylation state of the GluN2B subunit (NR2B) of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors, which are critical for synaptic plasticity and learning. GluN2B contains intracellular tyrosine residues, including Tyr1336. that undergo phosphorylation by Src-family kinases (e.g., Fyn). This post-translational modification modulates receptor trafficking, synaptic localization, and channel activity, influencing excitatory neurotransmission and neuronal signaling pathways.
The antibody specifically recognizes GluN2B when phosphorylated at Tyr1336. enabling researchers to investigate dynamic changes in receptor regulation under physiological or pathological conditions. It is widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunoprecipitation to assess phosphorylation-dependent interactions or activity in brain tissue, cultured neurons, or transfected cell models.
Studies utilizing this antibody have provided insights into NMDA receptor dysfunction linked to neurological disorders, including Alzheimer's disease, stroke, and epilepsy. Its specificity is typically validated through knockout controls or peptide competition assays. Researchers must optimize experimental conditions (e.g., fixation, antigen retrieval) to preserve phosphorylation epitopes during sample preparation. Proper controls, such as dephosphorylation treatments, are essential to confirm signal specificity.
Overall, this antibody serves as a key reagent for probing activity-dependent NMDA receptor regulation and its role in synaptic adaptation or neurodegeneration.
×