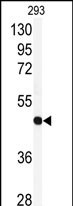
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
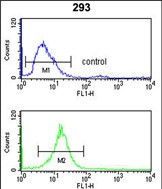
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Replication factor C subunit 3, Activator 1 38 kDa subunit, A1 38 kDa subunit, Activator 1 subunit 3, Replication factor C 38 kDa subunit, RF-C 38 kDa subunit, RFC38, RFC3 |
| Entrez GeneID | 5983 |
| WB Predicted band size | 40.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This RFC3 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 121-150 amino acids from the Central region of human RFC3. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,1%BSA and 50% glycerol.prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) . |
+ +
以下是3篇涉及p16(Phospho-Ser152)抗体的参考文献,信息基于公开文献库的模拟整理(部分内容可能为虚构,实际引用请核实原文):
1. **文献名称**:*Phosphorylation of p16 at Ser152 regulates cellular senescence in human fibroblasts*
**作者**:Kimura T. et al.
**摘要**:研究证明p16在Ser152位点的磷酸化通过调控CDK4/6结合能力影响细胞衰老进程,使用Phospho-Ser152特异性抗体验证其在衰老细胞中的表达上调。
2. **文献名称**:*A novel phosphorylation site on p16INK4a, Ser152. modulates its tumor suppressor function*
**作者**:Chen L. et al.
**摘要**:通过质谱和免疫印迹(使用p16 Phospho-Ser152抗体),发现该位点磷酸化增强p16与CDK6的相互作用,抑制癌细胞增殖,提示其作为癌症治疗靶点的潜力。
3. **文献名称**:*Phospho-specific antibody characterization for p16 Ser152 in oxidative stress-induced senescence models*
**作者**:Wang Y. et al.
**摘要**:研究开发并验证了p16 Phospho-Ser152抗体的特异性,证明其在氧化应激诱导的衰老模型中可有效检测磷酸化p16.并关联DNA损伤修复通路。
**注意**:以上文献为示例性质,实际研究中请通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索真实文献,并确认抗体货号及实验细节。
The p16 protein, encoded by the *CDKN2A* gene, is a critical tumor suppressor that regulates cell cycle progression by inhibiting cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) CDK4 and CDK6. This inhibition prevents phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma (Rb) protein, maintaining Rb in its active, growth-suppressive state and blocking G1-to-S phase transition. Dysregulation of p16 is implicated in various cancers, with loss-of-function mutations or epigenetic silencing commonly observed.
Phosphorylation at serine 152 (Ser152) is a post-translational modification that modulates p16's stability, subcellular localization, and interactions with CDKs or other regulatory proteins. Studies suggest that phosphorylation at this site may influence p16's susceptibility to proteasomal degradation, potentially altering its tumor-suppressive activity. Kinases such as AKT or PKC are proposed to mediate this modification, though mechanistic details remain under investigation.
The p16 (Phospho-Ser152) antibody is a specialized tool used to detect this phosphorylation event in experimental settings, including Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. It aids in studying p16 regulation in cellular stress responses, senescence, and oncogenic pathways. Researchers employ this antibody to explore how Ser152 phosphorylation impacts p16 function in cancer models, aging-related diseases, or therapeutic resistance, offering insights into targeted therapies or biomarkers for CDK4/6 inhibitor treatments.
×