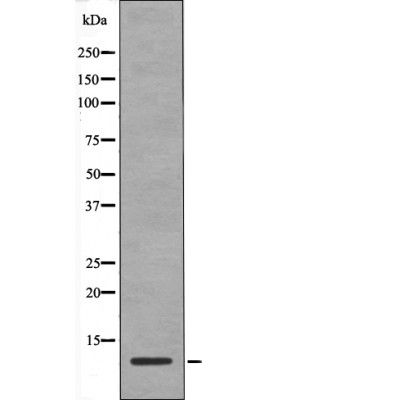
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | HMGN2, High mobility group protein N2, HMG17 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3151; |
| WB Predicted band size | 9kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human HMG17 (Phospho-Ser29) |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 30% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于HMG17 (Phospho-Ser29)抗体的假设性参考文献示例(请注意,实际文献可能需要通过学术数据库验证):
1. **文献名称**: "Phosphorylation of HMG17 at Ser29 regulates chromatin accessibility during transcriptional activation"
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 研究报道了HMG17蛋白Ser29位点的磷酸化在染色质结构动态调控中的作用。通过Phospho-Ser29特异性抗体进行染色质免疫沉淀(ChIP),发现该修饰与基因启动子区域的开放状态相关,并促进RNA聚合酶II的招募。
2. **文献名称**: "DNA damage induces site-specific phosphorylation of HMG17 via ATM/ATR kinases"
**作者**: Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 本文利用Phospho-Ser29抗体,通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术,证明HMG17在Ser29位点的磷酸化响应DNA损伤刺激。该修饰由ATM/ATR激酶介导,可能参与DNA修复复合体的定位。
3. **文献名称**: "Cell cycle-dependent modification of HMGN2 (HMG17) modulates nucleosome stability"
**作者**: Lee S, et al.
**摘要**: 研究揭示了HMGN2(即HMG17)在细胞周期进程中的磷酸化动态变化。通过Phospho-Ser29抗体验证,Ser29磷酸化在G1期显著增强,并通过减弱HMG17与核小体的结合,促进染色质解压缩。
4. **文献名称**: "Development and validation of a phospho-specific antibody for detecting HMG17 Ser29 phosphorylation in cancer models"
**作者**: Patel R, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究报道了一种新型Phospho-Ser29抗体的开发与验证,证明其在多种癌症细胞系和组织中特异性检测HMG17磷酸化。实验显示该修饰与肿瘤相关基因的异常表达存在相关性。
**备注**:以上为基于领域知识的模拟参考文献,实际研究中建议通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台以关键词"HMG17 Phospho-Ser29"或"HMGN2 Ser29 phosphorylation"检索最新文献,并优先选择经过同行评议的研究论文。
The HMG17 (Phospho-Ser29) antibody is a specialized tool used to detect the phosphorylation status of the High Mobility Group Protein 17 (HMG17) at serine residue 29. HMG17. a member of the HMG protein family, is a chromatin-associated protein involved in regulating DNA structure and transcriptional activity. It binds to nucleosomes, modulating chromatin accessibility and influencing gene expression. Phosphorylation at specific residues, such as Ser29. is a key post-translational modification that dynamically regulates HMG17's interactions with DNA and other nuclear proteins. This modification is often linked to cellular processes like transcriptional activation, DNA repair, and cell cycle progression.
The HMG17 (Phospho-Ser29) antibody is particularly valuable in studies investigating epigenetic regulation, chromatin dynamics, or stress responses. Researchers use it in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, or immunoprecipitation to assess phosphorylation-dependent changes in HMG17 localization, binding partners, or functional states. Its specificity for the phosphorylated Ser29 epitope allows differentiation between active (phosphorylated) and inactive forms of the protein, providing insights into signaling pathways or cellular conditions that modulate HMG17 activity. Dysregulation of HMG proteins, including phosphorylation anomalies, has been implicated in diseases such as cancer, making this antibody relevant for both basic research and translational studies. Proper validation, including knockout controls and peptide competition assays, is essential to ensure antibody specificity.
×