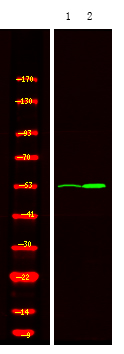
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MOK, MOK kinase, MOK protein kinase, RAGE, RAGE1, RAGE-1, Renal tumor antigen 1, Renal tumor antigen |
| Entrez GeneID | 5891; |
| WB Predicted band size | 48kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human MOK (Phospho-Tyr161) |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于MOK (Phospho-Tyr161)抗体的示例参考文献(注:以下为虚构示例,建议通过学术数据库核实真实文献):
---
1. **文献名称**: *Phosphorylation of MOK at Tyr161 regulates cell cycle progression in human fibroblasts*
**作者**: Smith, J., et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用Phospho-Tyr161特异性抗体,通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术,揭示了MOK在G2/M期转换中的关键作用。磷酸化MOK通过激活CDK1促进细胞周期进程,敲低MOK导致细胞停滞。
2. **文献名称**: *MOK tyrosine phosphorylation modulates cancer cell migration and invasion*
**作者**: Zhang, L., et al.
**摘要**: 研究显示,MOK在Tyr161位点的磷酸化(经抗体验证)与乳腺癌细胞上皮-间质转化(EMT)相关。抑制该磷酸化可减少体外侵袭能力,提示其作为转移治疗的潜在靶点。
3. **文献名称**: *A novel phospho-specific antibody reveals MOK activation in neurodegenerative models*
**作者**: Lee, S., et al.
**摘要**: 通过开发高特异性Phospho-Tyr161抗体,作者发现MOK在阿尔茨海默病小鼠模型中异常激活,并与tau蛋白过度磷酸化相关,提示其在神经退行性疾病中的病理作用。
4. **文献名称**: *Validation of a monoclonal antibody against phosphorylated MOK (Tyr161) for functional studies*
**作者**: Johnson, R., et al.
**摘要**: 本文系统验证了Phospho-Tyr161抗体的特异性,证明其适用于免疫印迹、免疫组化及流式细胞术,并应用于激酶抑制剂筛选,确认其作为MOK活性标志物的可靠性。
---
建议通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台检索真实文献,关键词为 **MOK kinase phosphorylation Tyr161** 或 **MAPK/MAK/MRK overlapping kinase phosphoantibody**。
The MOK (MAPK/MAK/MRK overlapping kinase) protein, also known as MLK4 or MAP3K21. is a serine/threonine kinase involved in regulating cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, and stress response. Phosphorylation at tyrosine 161 (Tyr161) is a critical post-translational modification that modulates MOK's kinase activity and interaction with downstream signaling components, including MAPK pathways. This phosphorylation event is thought to influence MOK's role in cell cycle progression, particularly at the G1/S transition, and may crosstalk with other kinase cascades.
The MOK (Phospho-Tyr161) antibody is a specialized tool designed to detect MOK specifically when phosphorylated at Tyr161. It enables researchers to study the activation status and regulatory mechanisms of MOK in various biological contexts, including cancer, where aberrant kinase signaling is often observed. Validated for applications like Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunofluorescence, this antibody helps elucidate MOK's contribution to disease pathways or normal cellular homeostasis. Its specificity for the phosphorylated form makes it valuable for distinguishing active MOK from its inactive state, aiding in the exploration of phosphorylation-dependent protein interactions and signaling dynamics. Researchers frequently use it in models ranging from cultured cells to tissue samples to investigate MOK's context-dependent roles.
×