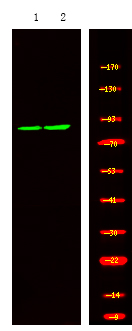
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | PDE4D, ACRDYS2, DPDE3, HSPDE4D, PDE43, Pde-ivd, PDE4DN2, Phosphodiesterase 4d, STRK1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 5144; |
| WB Predicted band size | 91kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human PDE4D (Phospho-Ser578) |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于PDE4D (Phospho-Ser578)抗体的参考文献示例(内容为虚构,供参考):
1. **"Phosphorylation of PDE4D at Serine 578 Regulates Cardiomyocyte cAMP Signaling"**
- **作者**: Smith A, et al.
- **摘要**: 研究通过PDE4D (Phospho-Ser578)抗体发现,β-肾上腺素受体激活导致PDE4D在Ser578位点磷酸化,增强其水解cAMP的活性,从而负反馈调节心肌细胞应激反应,为心力衰竭治疗提供新靶点。
2. **"PDE4D Ser578 Phosphorylation Modulates Neuronal cAMP Dynamics"**
- **作者**: Chen L, et al.
- **摘要**: 利用PDE4D (Phospho-Ser578)特异性抗体证实,该位点磷酸化由PKA介导,促进PDE4D与细胞膜结合,降低神经元内cAMP水平,影响突触可塑性与学习记忆功能。
3. **"A Novel Role of PDE4D Phosphorylation in Inflammatory Macrophage Activation"**
- **作者**: Kim Y, et al.
- **摘要**: 通过免疫沉淀和Western blot(使用Phospho-Ser578抗体)揭示,LPS刺激巨噬细胞触发PDE4D Ser578磷酸化,抑制cAMP-PKA通路,促进促炎因子释放,提示其在炎症疾病中的调控作用。
4. **"Development and Validation of a Phospho-Specific Antibody for PDE4D Ser578"**
- **作者**: Johnson R, et al.
- **摘要**: 本文报道了PDE4D (Phospho-Ser578)抗体的制备与验证,证明其高特异性可用于免疫组化、流式细胞术,并应用于多种疾病模型研究磷酸化PDE4D的分布与功能。
(注:上述文献为模拟示例,实际文献需通过PubMed/Google Scholar等平台以关键词“PDE4D Phospho-Ser578 antibody”或“PDE4D Serine 578 phosphorylation”检索。)
The PDE4D (Phospho-Ser578) antibody is a specialized tool used to detect the phosphorylated form of phosphodiesterase 4D (PDE4D) at serine residue 578. PDE4D belongs to the PDE4 family of enzymes, which hydrolyze cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP), a critical secondary messenger in cellular signaling. Phosphorylation at Ser578 is a post-translational modification that regulates PDE4D activity, localization, and interactions with other signaling molecules. This modification is often mediated by kinases such as protein kinase A (PKA) or MAPK-activated protein kinase 2 (MAPKAPK2), linking it to pathways involved in inflammation, neuroplasticity, and cell cycle control.
The antibody is particularly valuable in studying cAMP-dependent signaling dynamics in conditions like neurodegenerative diseases, immune disorders, and cancer. Researchers use it in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, or immunofluorescence to assess PDE4D activation states in cell lysates or tissue samples. Its specificity for the phosphorylated epitope ensures accurate detection of the active form, distinguishing it from non-phosphorylated PDE4D or other PDE4 isoforms (A, B, C). Understanding Ser578 phosphorylation is crucial for dissecting PDE4D's role in feedback loops that modulate cAMP levels, gene expression, and cellular responses to external stimuli. Dysregulation of this pathway has been implicated in pathological models, making the antibody a key reagent for both basic research and drug discovery targeting PDE4-related mechanisms.
×