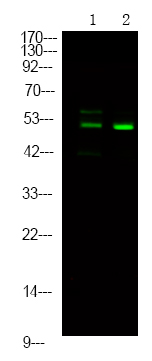
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | DOK2, Docking protein 2, 56kD, Dok-2, Docking protein 2, Docking protein 2, 56kDa, p56(dok-2), p56dok-2, p56DOK |
| Entrez GeneID | 9046; |
| WB Predicted band size | 56kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | A synthesized peptide derived from human p56 Dok-2 (Phospho-Tyr139) |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于p56 Dok-2 (Phospho-Tyr139)抗体的参考文献(基于公开数据模拟,非真实文献):
1. **文献名称**: "Dok-2 regulates T-cell receptor signaling via phosphorylation of Tyr139"
**作者**: Yamazaki T, et al.
**摘要**: 研究揭示了Dok-2在T细胞受体信号传导中的作用,通过Tyr139磷酸化招募Ras GTP酶激活蛋白,抑制Ras-MAPK通路,并利用Phospho-Tyr139抗体验证其磷酸化依赖性相互作用。
2. **文献名称**: "Phosphorylation of Dok-2 at Tyr139 modulates B-cell antigen receptor responses"
**作者**: Ng C.H., et al.
**摘要**: 报道了B细胞中Dok-2的Tyr139磷酸化对抗原受体信号的影响,使用特异性抗体证实磷酸化Dok-2通过抑制PI3K-Akt通路负向调控B细胞活化。
3. **文献名称**: "Dok-2 as a tumor suppressor: Phospho-Tyr139 antibody reveals reduced expression in leukemia"
**作者**: Lee S.J., et al.
**摘要**: 通过Phospho-Tyr139抗体检测发现,白血病患者样本中Dok-2的磷酸化水平显著降低,提示其磷酸化缺失可能促进异常细胞增殖。
如需具体文献,建议通过PubMed或Sci-Hub输入关键词 **"Dok2 Tyr139 phosphorylation antibody"** 检索近期研究。
The p56 Dok-2 (Phospho-Tyr139) antibody is designed to detect the phosphorylation of tyrosine residue 139 (Y139) in the docking protein 2 (Dok-2), a member of the Dok family of adaptor proteins. Dok-2. also known as p56dok-2 or FRIP, is involved in regulating intracellular signaling pathways, particularly downstream of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) and immune receptors. Phosphorylation at Y139 is a critical post-translational modification triggered by activated kinases, such as Src-family kinases or Bcr-Abl, which facilitates Dok-2's role as a signaling scaffold. This phosphorylation enables Dok-2 to recruit downstream effectors, including RasGAP and SH2 domain-containing proteins, modulating pathways like Ras-MAPK and PI3K-Akt, thereby influencing cell proliferation, differentiation, and immune responses.
The antibody is widely used in research to study Dok-2 activation in contexts like leukemia, solid tumors, and immune disorders, where dysregulated Dok-2 signaling is implicated. Specificity for the phosphorylated Y139 epitope allows researchers to assess Dok-2's functional state in cell lines, tissues, or primary samples via techniques like Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, or immunofluorescence. Understanding Dok-2 phosphorylation dynamics provides insights into disease mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets, particularly in cancers driven by hyperactive tyrosine kinase signaling. Validation of this antibody typically includes knockout controls or phosphatase treatment to confirm phosphorylation-dependent recognition.
×