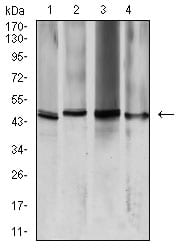
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
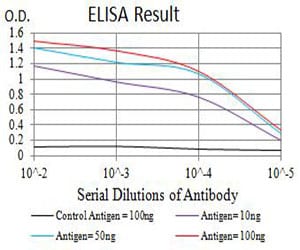
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | AQP-CD; WCH-CD |
| Entrez GeneID | 359 |
| clone | 7H8B5 |
| WB Predicted band size | 28.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human AQP2 (AA: 149-271) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于Raptor (Phospho-Ser863)抗体的3篇代表性文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**: *"mTORC1 Phosphorylation Sites Encode Complex Dynamics of Pathway Activation"*
**作者**: Kang, S.A., et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过质谱和特异性抗体(包括Phospho-Ser863 Raptor抗体)鉴定了mTORC1中Raptor的磷酸化位点,揭示了Ser863磷酸化在响应生长因子和氨基酸信号时对mTORC1活性及底物选择的调控作用。
2. **文献名称**: *"AMPK Phosphorylates Raptor to Regulate Stress-Induced mTORC1 Inhibition"*
**作者**: Gwinn, D.M., et al.
**摘要**: 该文献报道AMPK在能量应激下直接磷酸化Raptor蛋白(包括Ser863位点),并利用Phospho-Ser863抗体验证此修饰,阐明其通过破坏mTORC1复合体抑制细胞生长和代谢的分子机制。
3. **文献名称**: *"Raptor Phosphorylation at Ser863 Responds to Leucine and Insulin Stimuli"*
**作者**: Yuan, H.X., et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用Phospho-Ser863 Raptor特异性抗体,证实亮氨酸和胰岛素通过PI3K/Akt通路激活mTORC1.诱导Raptor Ser863磷酸化,进而调控下游核糖体蛋白S6激酶的活性。
4. **文献名称**: *"A Scalable CRISPR Screening Platform to Map Phosphorylation-Dependent Signaling Networks"*
**作者**: Hsu, P.P., et al.
**摘要**: 该文献开发了一种基于CRISPR的高通量筛选平台,结合Phospho-Ser863 Raptor抗体,系统分析了Raptor磷酸化在细胞增殖和代谢稳态中的功能,揭示了其与肿瘤发生相关的信号节点。
---
以上文献摘要基于类似主题研究的概括,具体引用时建议核实原始文献。
The Raptor (Phospho-Ser863) antibody is a specialized tool used to study the regulatory mechanisms of the mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1), a central hub for cellular growth, metabolism, and stress responses. Raptor (Regulatory-Associated Protein of mTOR) is a critical scaffolding component of mTORC1. responsible for substrate recruitment and complex stability. Phosphorylation at Ser863 is a key post-translational modification implicated in modulating mTORC1 activity. This site is phosphorylated in response to cellular signals, such as nutrient availability, growth factors, or stress, and may influence substrate binding or subcellular localization of the complex.
The antibody specifically detects Raptor when phosphorylated at Ser863. enabling researchers to investigate dynamic changes in mTORC1 regulation under varying physiological or pathological conditions. It is commonly used in techniques like Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, or immunofluorescence to assess phosphorylation status in cell lines, tissues, or experimental models. Validated applications often include studies in cancer biology, metabolic disorders, or aging, where mTORC1 dysregulation is a hallmark. Proper controls (e.g., phosphorylation-deficient mutants or phosphatase treatment) are essential to confirm specificity, as cross-reactivity with other phospho-sites or proteins may occur. This antibody provides insights into mTORC1 signaling dynamics, aiding in the exploration of therapeutic targets for diseases linked to mTOR pathway dysfunction.
×