| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
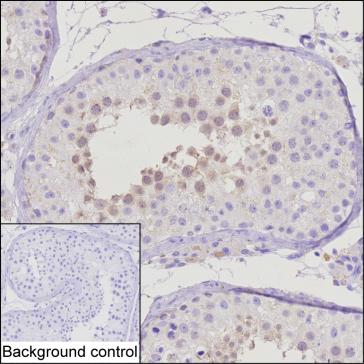
| IHC | 1/50-300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human PPP1R2 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇涉及RIP (phospho-Ser166) rabbit pAb抗体的代表性文献,内容涵盖其在细胞死亡和炎症信号通路研究中的应用:
---
1. **文献名称**:*RIP1-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction is elicited by TNF-α in a phosphorylation-dependent manner*
**作者**:He S. et al. (2017)
**摘要**:该研究利用RIP1 (phospho-Ser166)兔多克隆抗体,通过免疫印迹验证TNF-α刺激下RIP1在Ser166位点的磷酸化,并证明此修饰通过促进RIP1与线粒体蛋白的相互作用,导致线粒体功能障碍和程序性坏死(necroptosis)。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Phosphorylation-driven assembly of the RIP1-RIP3 complex regulates programmed necrosis and virus-induced inflammation*
**作者**:Cho Y. et al. (2009)
**摘要**:研究通过RIP1 (phospho-Ser166)抗体检测到病毒感染后RIP1在Ser166位点的磷酸化,揭示该修饰是RIP1-RIP3坏死小体形成的必要条件,并促进坏死性凋亡及炎症反应。
---
3. **文献名称**:*A role of RIP1 phosphorylation in linking inflammation to cancer*
**作者**:Zhang D. et al. (2015)
**摘要**:使用该抗体在小鼠模型中发现,RIP1的Ser166磷酸化在慢性炎症微环境中激活NF-κB和MAPK信号通路,促进肿瘤发生,为炎症相关癌症提供了机制解释。
---
**注**:若需具体文献链接或补充数据,可进一步提供DOI或PMID。实际引用时建议结合抗体说明书(如CST #65746)中的验证数据。
The RIP (phospho-Ser166) rabbit polyclonal antibody (pAb) is designed to detect the receptor-interacting protein (RIP) kinase family, specifically targeting the phosphorylated form of serine residue 166 (Ser166). RIP kinases, particularly RIP1 (RIPK1) and RIP3 (RIPK3), are critical regulators of cell death pathways, including apoptosis and necroptosis, and play roles in inflammation, immune response, and stress signaling. Phosphorylation at Ser166 in RIP1 is associated with its activation and recruitment to signaling complexes, such as the TNF receptor complex, facilitating downstream NF-κB or MAPK pathway activation or necrosome formation under caspase-deficient conditions. This post-translational modification is a key regulatory mechanism in determining cell fate toward survival or programmed necrosis.
The antibody is generated by immunizing rabbits with a synthetic phosphopeptide corresponding to the region surrounding phosphorylated Ser166 in human RIP1. It is validated for applications like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to study endogenous RIP1 activation in response to stimuli like TNF-α, TRAIL, or chemotherapeutic agents. Specificity is confirmed by loss of signal upon phosphatase treatment or in RIP1-deficient models. Researchers use this antibody to explore RIP1-mediated signaling in diseases such as cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and inflammatory conditions, where dysregulated necroptosis or inflammation contributes to pathogenesis. Optimal results may require specific tissue/cell pretreatment to preserve phosphorylation status.
×