| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
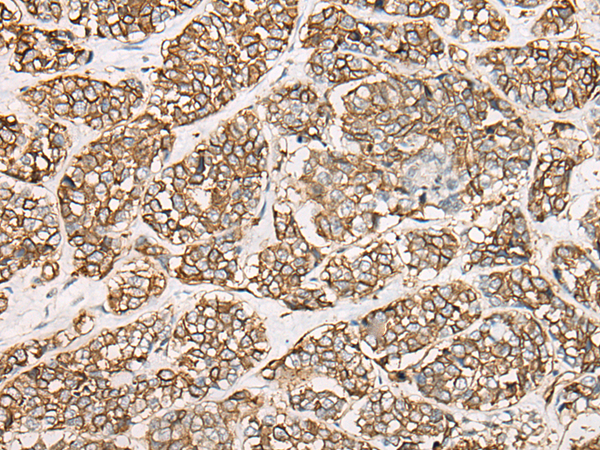
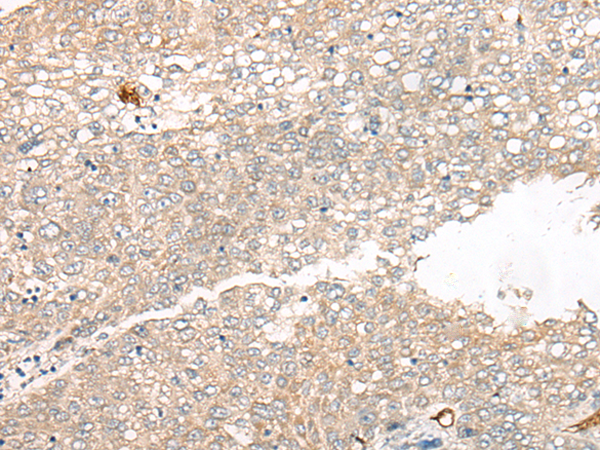
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CO; CHIP28; AQP-CHIP |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human AQP1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于AQP1抗体的代表性文献及其摘要内容概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"Selective reduction of renal aquaporin-1 expression during cisplatin-induced acute renal failure in mice"*
**作者**:King LS et al.
**摘要**:研究利用AQP1特异性抗体,通过免疫组化和Western Blot分析小鼠肾脏中AQP1的表达变化,发现顺铂诱导的急性肾损伤中AQP1蛋白水平显著下降,提示其与肾小管功能损伤相关。
---
2. **文献名称**:*"Aquaporin-1 facilitates epithelial cell migration in colorectal cancer via modulation of actin dynamics"*
**作者**:Endo Y et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫荧光和AQP1抗体标记,揭示了AQP1在结直肠癌组织中的高表达,并证明其通过调节细胞骨架动力学促进肿瘤细胞迁移,为癌症治疗提供潜在靶点。
---
3. **文献名称**:*"Characterization of a polyclonal antibody to aquaporin-1 for immunocytochemical localization in mammalian tissues"*
**作者**:Nielsen S et al.
**摘要**:报道了一种兔源多克隆AQP1抗体的开发与验证,证明其在肾脏、肺和血管内皮中的特异性染色能力,为后续研究提供了可靠的检测工具。
---
4. **文献名称**:*"Aquaporin-1 deficiency impairs tumor angiogenesis and growth in a murine model of lung cancer"*
**作者**:Saadoun S et al.
**摘要**:利用AQP1敲除小鼠和抗体标记技术,发现AQP1缺失导致肿瘤血管生成减少,表明AQP1在肿瘤微环境中的促血管生成作用。
---
这些文献涵盖了AQP1抗体在疾病机制研究、抗体开发验证及临床应用中的关键作用。
**Background of AQP1 Antibody**
Aquaporin-1 (AQP1) is a small integral membrane protein belonging to the aquaporin family, first identified in 1988. It facilitates the selective transport of water across cell membranes, playing a critical role in maintaining water homeostasis in various tissues, including the kidneys, lungs, blood vessels, and eyes. AQP1 forms tetrameric channels in membranes, enabling rapid water flux driven by osmotic gradients.
Antibodies targeting AQP1 are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function. These antibodies are widely used in techniques like immunohistochemistry (IHC), Western blotting, and immunofluorescence to detect AQP1 in tissue sections or cultured cells. AQP1 dysregulation has been implicated in pathological conditions such as edema, cancer (via angiogenesis), and renal disorders. For instance, reduced AQP1 expression in renal tubules correlates with impaired urine concentration, while its overexpression in tumors may promote metastasis.
Research applications of AQP1 antibodies also extend to exploring therapeutic interventions. Inhibiting AQP1 in preclinical models has shown potential in limiting tumor growth or fluid retention. However, challenges remain in ensuring antibody specificity, as cross-reactivity with other aquaporins can occur. Validated AQP1 antibodies are thus crucial for accurate experimental outcomes. Overall, AQP1 antibodies serve as vital reagents in both basic research and clinical investigations, advancing our understanding of water transport mechanisms and related diseases.
×