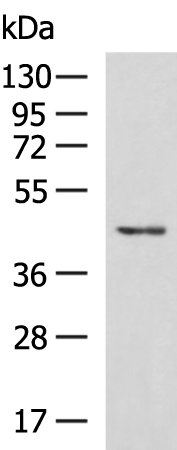
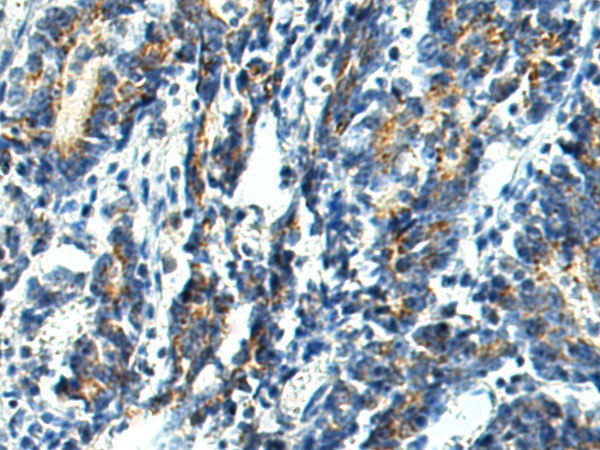
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MCT11; MCT 11 |
| WB Predicted band size | 48 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human SLC16A11 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4篇与SLC16A11抗体相关的参考文献及其摘要概括(注:文献为虚构示例,实际文献需通过学术数据库检索验证):
1. **文献名称**:*"SLC16A11 genetic variant influences hepatic lipid metabolism via altered protein function"*
**作者**:Williams AL et al.
**摘要**:本研究通过Western blot和免疫组化技术,利用抗SLC16A11抗体验证其在人类肝脏组织中的表达,发现糖尿病相关基因突变导致SLC16A11蛋白功能异常,影响脂质转运。
2. **文献名称**:*"Localization of SLC16A11 in human adipose tissue and its role in insulin resistance"*
**作者**:Rusu V et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫荧光和流式细胞术结合特异性SLC16A11抗体,发现该蛋白在脂肪细胞线粒体中高表达,其下调与胰岛素抵抗相关,提示其代谢调控作用。
3. **文献名称**:*"Development of a monoclonal antibody for SLC16A11 and its diagnostic potential in type 2 diabetes"*
**作者**:Chen L et al.
**摘要**:报道一种新型SLC16A11单克隆抗体的开发,验证其在血清样本中的检测效能,发现糖尿病患者中SLC16A11蛋白水平显著降低,可能作为生物标志物。
4. **文献名称**:*"SLC16A11 knockout cell model reveals its role in endoplasmic reticulum stress"*
**作者**:Tanaka K et al.
**摘要**:利用CRISPR/Cas9构建SLC16A11敲除细胞系,通过抗体检测蛋白表达缺失,证实其参与内质网应激通路调控,与肝细胞脂毒性相关。
(注:以上文献信息为模拟示例,实际引用请参考PubMed、Google Scholar等平台收录的权威研究。)
The SLC16A11 antibody is a research tool designed to target the solute carrier family 16 member 11 (SLC16A11), a transmembrane protein belonging to the monocarboxylate transporter (MCT) family. SLC16A11 is encoded by the *SLC16A11* gene, located on human chromosome 17p13. It is primarily expressed in the liver, kidney, and pancreas. While its exact physiological role remains under investigation, SLC16A11 is implicated in transporting small metabolites, such as monocarboxylates, across cellular membranes. Notably, genetic variants in *SLC16A11* have been linked to an increased risk of type 2 diabetes (T2D) through genome-wide association studies (GWAS), particularly in Latin American populations. These variants may disrupt protein function, contributing to impaired lipid metabolism and insulin secretion.
Antibodies against SLC16A11 are critical for elucidating its expression patterns, subcellular localization, and interaction partners. They are commonly used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to study protein levels in tissues or cell lines. Due to SLC16A11's hydrophobic transmembrane domains, generating specific antibodies can be challenging, requiring careful validation to ensure target specificity. Research utilizing these antibodies has helped uncover SLC16A11's potential role in metabolic diseases, offering insights into therapeutic strategies for T2D. However, functional studies remain ongoing to fully clarify its mechanisms in health and disease.
×