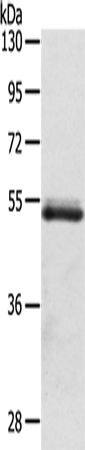
| WB | 1/200-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GC1; OLM4; OlfD; GW112; hGC-1; hOLfD; UNQ362; bA209J19.1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 57 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human OLFM4 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于OLFM4抗体的3篇代表性文献,简要总结如下:
---
1. **文献名称**:*OLFM4 is a robust marker for stem cells in human intestine and marks a subset of colorectal cancer cells*
**作者**:van der Flier, L.G. et al. (2009)
**摘要**:该研究在《胃肠病学》(*Gastroenterology*)中报道了OLFM4抗体在肠道干细胞标记中的应用,证实其与Lgr5标记的干细胞共定位,并发现其在结直肠癌中的异质性表达,提示其作为癌症干细胞标志物的潜力。
---
2. **文献名称**:*OLFM4 is a novel extracellular matrix protein expressed in myeloid precursors and tumors*
**作者**:Liu, W. et al. (2010)
**摘要**:发表于《美国病理学杂志》(*American Journal of Pathology*),研究通过OLFM4抗体检测发现其在髓系前体细胞和多种实体瘤(如前列腺癌、胃癌)中的高表达,并揭示其通过调控细胞黏附通路影响肿瘤进展。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Production and characterization of a monoclonal antibody specific for human OLFM4*
**作者**:Koh, I. et al. (2012)
**摘要**:该技术性研究在《单克隆抗体杂志》(*mAbs*)中详细描述了小鼠抗人OLFM4单克隆抗体的开发,验证其特异性用于流式细胞术和免疫组化,并应用于白血病细胞和肠黏膜样本的检测。
---
**备注**:以上文献可通过PubMed或期刊官网检索全文。如需更近期研究(如OLFM4在急性髓系白血病或免疫微环境中的作用),建议补充关键词如“OLFM4 antibody biomarker”进一步查询。
OLFM4 (Olfactomedin-4), also known as GW112 or hGC-1. is a secreted glycoprotein belonging to the olfactomedin domain-containing protein family. Initially identified in hematopoietic stem cells, OLFM4 is implicated in cell adhesion, apoptosis regulation, and innate immune responses. Its expression is tissue-specific, notably observed in bone marrow, gastrointestinal tract, and prostate, and it serves as a granulocyte-specific marker during inflammation. Structurally, OLFM4 contains a signal peptide, N-terminal domain, and a C-terminal olfactomedin domain, which mediates protein-protein interactions.
OLFM4 antibodies are critical tools for detecting this protein in research and diagnostics. Studies link OLFM4 overexpression to several cancers, including colorectal, gastric, and prostate cancers, where it may promote tumor progression by inhibiting apoptosis or modulating signaling pathways like NF-κB. Conversely, reduced OLFM4 expression correlates with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), suggesting a dual role in inflammation and cancer.
Antibodies against OLFM4 are widely used in immunohistochemistry (IHC), Western blotting, and ELISA to study its localization, expression patterns, and clinical relevance. In diagnostics, OLFM4 antibodies aid in distinguishing certain cancer subtypes or assessing disease severity in IBD. Recent research also explores OLFM4 as a potential therapeutic target, driving interest in developing neutralizing antibodies or small-molecule inhibitors. Despite progress, its precise biological mechanisms remain under investigation, highlighting the continued importance of OLFM4 antibodies in unraveling its multifaceted roles.
×