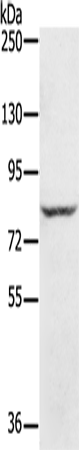
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | URCC; RNF124 |
| WB Predicted band size | 86 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human RNF43 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于RNF43抗体的代表性文献(格式:文献名称、作者、摘要内容简述):
---
1. **"RNF43 mutations in colorectal cancer: Molecular insights and therapeutic implications"**
- **作者**: Wu J. et al. (2013)
- **摘要**: 研究通过Western blot和免疫组化(使用RNF43特异性抗体)发现,结直肠癌中RNF43高频突变导致其蛋白表达缺失,进而抑制Wnt信号通路的负调控,促进肿瘤发生。
2. **"RNF43 ubiquitinates and degrades Wnt receptors to suppress pathway activity"**
- **作者**: Hao H.X. et al. (2014)
- **摘要**: 利用RNF43抗体进行免疫沉淀实验,证明RNF43通过泛素化修饰Wnt受体(如Frizzled),促进其溶酶体降解,从而负调控Wnt信号传导,为靶向治疗提供理论依据。
3. **"Loss of RNF43 expression predicts poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer"**
- **作者**: Jiang X. et al. (2018)
- **摘要**: 通过免疫组化(使用抗RNF43抗体)分析胰腺癌组织,发现RNF43蛋白表达缺失与患者生存率下降显著相关,提示其作为预后生物标志物的潜力。
---
以上文献均涉及RNF43抗体的实验应用(如检测蛋白表达、定位或功能研究),并探讨其在癌症中的分子机制或临床意义。如需更多文献或具体实验细节,可进一步缩小研究领域(如特定癌症类型或信号通路)。
RNF43 (Ring Finger Protein 43) is a transmembrane E3 ubiquitin ligase that plays a critical role in regulating Wnt signaling pathways, primarily by targeting Frizzled receptors for lysosomal degradation. First identified as a tumor suppressor, RNF43 is frequently mutated in various cancers, including colorectal, endometrial, and pancreatic carcinomas. Its dysfunction leads to uncontrolled Wnt/β-catenin signaling, driving cell proliferation and tumorigenesis. Antibodies targeting RNF43 are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and functional interactions in both normal physiology and disease contexts.
These antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to assess RNF43 protein levels in tissues or cell lines. Given RNF43’s role in cancer, its antibodies also aid in identifying loss-of-function mutations or downregulation associated with poor prognosis. Additionally, they support research exploring RNF43’s interplay with other Wnt regulators, such as ZNRF3. and its involvement in stem cell maintenance and tissue homeostasis. Challenges in antibody development include specificity due to post-translational modifications and shared epitopes within the RING domain family. Recent advances in monoclonal antibody engineering have improved detection reliability, facilitating translational studies aimed at targeting RNF43-related pathways for cancer therapy or diagnostic applications.
×