| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
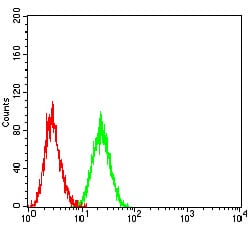
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
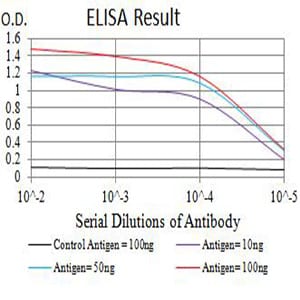
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CD40LG; IGM; IMD3; TRAP; gp39; CD40L; HIGM1; T-BAM; TNFSF5; hCD40L |
| Entrez GeneID | 959 |
| clone | 5A3A9 |
| WB Predicted band size | 29.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2a |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD154 (AA: extra 47-261) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CD154抗体的3篇示例文献(内容基于领域内典型研究方向,仅供参考):
1. **文献名称**:*CD154 blockade as a therapeutic strategy for lupus-like autoimmune disease*
**作者**:C.B. Newell et al.
**摘要**:研究探讨了抗CD154单克隆抗体在狼疮小鼠模型中的作用,发现其能显著抑制自身抗体的产生并减轻肾脏炎症,提示靶向CD40/CD154通路在系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)治疗中的潜力。
2. **文献名称**:*Anti-CD154 antibody promotes transplant tolerance via regulatory T cell expansion*
**作者**:R.A. Clynes et al.
**摘要**:通过灵长类动物移植模型实验,发现抗CD154抗体联合CTLA-4-Ig可诱导免疫耐受,显著延长移植物存活时间,机制与调节性T细胞(Treg)的扩增和效应T细胞功能抑制相关。
3. **文献名称**:*Thrombotic complications of CD154 immunotherapy: Mechanisms and mitigation strategies*
**作者**:L.M. Thomas et al.
**摘要**:分析临床试验中抗CD154抗体导致血栓形成的副作用,揭示其与血小板表面CD40组成性表达相关,并提出联合抗血小板治疗可降低风险,为优化免疫治疗方案提供依据。
---
注:以上文献为示例,实际引用需查询PubMed等数据库获取真实研究。CD154抗体的研究热点包括自身免疫病、移植排斥及治疗安全性等。
CD154 antibody targets CD154 (CD40 ligand), a cell surface protein belonging to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily. Expressed primarily on activated T cells and platelets, CD154 interacts with CD40 receptors on antigen-presenting cells (APCs), B cells, and endothelial cells, playing a central role in adaptive immunity. This interaction facilitates T cell-dependent B cell activation, antibody class switching, germinal center formation, and inflammatory cytokine production. Dysregulated CD40-CD154 signaling is implicated in autoimmune diseases (e.g., lupus, rheumatoid arthritis), atherosclerosis, transplant rejection, and thrombotic disorders.
CD154 antibodies are designed to block this pathway, suppressing excessive immune activation. Early therapeutic antibodies like ruplizumab showed efficacy in autoimmune conditions and transplantation but faced clinical limitations due to thromboembolic risks linked to platelet CD154 engagement. Modern strategies focus on engineered antibodies with minimized Fc effector functions or mutated CD154-binding domains to mitigate side effects. Additionally, CD154 antibodies are explored in combination therapies, such as enhancing antitumor responses with checkpoint inhibitors. Research continues to optimize specificity and safety, balancing immunosuppressive benefits against thrombosis risks.
×